It is not too late to achieve global covid-19 vaccine equity
- PMID: 35331982
- PMCID: PMC8943596
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2022-070650
It is not too late to achieve global covid-19 vaccine equity
Erratum in
-
It is not too late to achieve global covid-19 vaccine equity.BMJ. 2022 Mar 28;376:o812. doi: 10.1136/bmj.o812. BMJ. 2022. PMID: 35346945 No abstract available.
Abstract
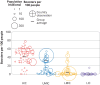
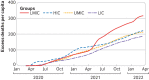
Gavin Yamey and colleagues say that a new, urgent push for global vaccine equity could help avert suffering and deaths, protect economies, and prevent new virus variants
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: GY was a member of the covid-19 vaccine development taskforce hosted by the World Bank, and participated as an unpaid academic adviser in the consultation process that led to the launch of Covax. He has received grant funding from WHO; Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance; and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. He is a funding member of Amnesty International, which is one of the members of the People’s Vaccine Alliance. PG participated as a member of the Data Safety and Monitoring Board for a phase 3 double blind, randomised, placebo controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of efficacy and safety in health professionals of the adsorbed vaccine covid-19 (inactivated) produced by Sinovac (study implemented by BUTANTAN in Brazil). FH is a member of the People’s Vaccine Alliance and serves on the advisory group of Resolve to SAVE Lives. WM has received research funding from WHO and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. KKM was a member of the covid-19 vaccine development taskforce hosted by the World Bank and has received funding from WHO and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. MP is an adviser to non-profit organisations such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, WHO, Stop TB Partnership, and Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics; he has no financial or industry disclosures. SS has no competing interests. PS has contributed to this article in a personal capacity unconnected to his duties as an employee of the World Bank Group and has provided analytical and other inputs based on the data analytics resource pandem-ic.com that he also developed in a personal capacity. AT has received research funding through Duke University and Duke affiliated non-profit Innovations in Healthcare from Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, The Rockefeller Foundation, USAID, Grand Challenges Canada, and Pfizer Foundation. KU has received research funding through Duke University and Duke affiliated non-profit Innovations in Healthcare from Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, The Rockefeller Foundation, USAID, Grand Challenges Canada, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Johnson and Johnson Foundation, Medtronic, Pfizer, Pfizer Foundation, Takeda, and Vynamic. He has served as unpaid adviser for the Hewlett Foundation and Africa CDC, and has received an honorarium from Weber Shandwick.
Figures

References
-
- Glassman A, Kenny C, Yang G. Covid-19 vaccine development and rollout in historical perspective. Center for Global Development. Feb 2022. Report no 607. https://www.cgdev.org/publication/covid-19-vaccine-development-and-rollo...
-
- Byanyima W. A global vaccine apartheid is unfolding. People’s lives must come before profit. Guardian 2021 Jan 29. https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2021/jan/29/a-global-vacc...
-
- Ritchie H, Mathieu E, Rodés-Guirao L, et al. Coronavirus vaccinations (COVID-19). Our World in Data 2020. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
