Supervised machine learning for automatic classification of in vivo scald and contact burn injuries using the terahertz Portable Handheld Spectral Reflection (PHASR) Scanner
- PMID: 35332207
- PMCID: PMC8948290
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08940-4
Supervised machine learning for automatic classification of in vivo scald and contact burn injuries using the terahertz Portable Handheld Spectral Reflection (PHASR) Scanner
Abstract
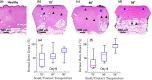
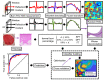
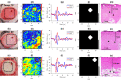
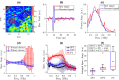
We present an automatic classification strategy for early and accurate assessment of burn injuries using terahertz (THz) time-domain spectroscopic imaging. Burn injuries of different severity grades, representing superficial partial-thickness (SPT), deep partial-thickness (DPT), and full-thickness (FT) wounds, were created by a standardized porcine scald model. THz spectroscopic imaging was performed using our new fiber-coupled Portable HAndheld Spectral Reflection Scanner, incorporating a telecentric beam steering configuration and an f-[Formula: see text] scanning lens. ASynchronous Optical Sampling in a dual-fiber-laser THz spectrometer with 100 MHz repetition rate enabled high-speed spectroscopic measurements. Given twenty-four different samples composed of ten scald and ten contact burns and four healthy samples, supervised machine learning algorithms using THz-TDS spectra achieved areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves of 0.88, 0.93, and 0.93 when differentiating between SPT, DPT, and FT burns, respectively, as determined by independent histological assessments. These results show the potential utility of our new broadband THz PHASR Scanner for early and accurate triage of burn injuries.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MHA discloses intellectual property owned by the University of Washington, US Patent No. US9295402B1. The rest of the authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Accurate and early prediction of the wound healing outcome of burn injuries using the wavelet Shannon entropy of terahertz time-domain waveforms.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Nov;27(11):116001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.11.116001. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36348509 Free PMC article.
-
Deep neural network classification of in vivo burn injuries with different etiologies using terahertz time-domain spectral imaging.Biomed Opt Express. 2022 Mar 3;13(4):1855-1868. doi: 10.1364/BOE.452257. eCollection 2022 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 35519269 Free PMC article.
-
Terahertz Portable Handheld Spectral Reflection (PHASR) Scanner.IEEE Access. 2020;8:228024-228031. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3045460. Epub 2020 Dec 17. IEEE Access. 2020. PMID: 35433151 Free PMC article.
-
Research Advances in Terahertz Technology for Skin Detection.Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2025 Jan;43(1):1-7. doi: 10.1089/photob.2024.0079. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2025. PMID: 39841526 Review.
-
Machine Learning Techniques for THz Imaging and Time-Domain Spectroscopy.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 8;21(4):1186. doi: 10.3390/s21041186. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33567605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiresolution spectrally-encoded terahertz reflection imaging through a highly diffusive cloak.Opt Express. 2022 Aug 29;30(18):31550-31566. doi: 10.1364/OE.463599. Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 36242235 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Corneal Endothelial Damage Using Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy and Support Vector Machines.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;22(23):9071. doi: 10.3390/s22239071. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501773 Free PMC article.
-
Terahertz PHASR Scanner with 2 kHz, 100 picosecond Time-Domain Trace Acquisition Rate and an Extended Field-of-View Based on a Heliostat Design.IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol. 2022 Nov;12(6):619-632. doi: 10.1109/tthz.2022.3200210. Epub 2022 Aug 22. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36531441 Free PMC article.
-
Review of machine learning for optical imaging of burn wound severity assessment.J Biomed Opt. 2024 Feb;29(2):020901. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.2.020901. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 38361506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triage of in vivo burn injuries and prediction of wound healing outcome using neural networks and modeling of the terahertz permittivity based on the double Debye dielectric parameters.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Jan 30;14(2):918-931. doi: 10.1364/BOE.479567. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 36874480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cairns, C., Kang, K. & Santo, L. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2018 Emergency Department Summary Tables. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhamcs/web_tables/2018-ed-web-tables-508.pdf (2018).
-
- Mertens DM, Jenkins ME, Warden GD. Outpatient burn management. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 1997;32:343. - PubMed
-
- Baxter CR. Management of burn wounds. Dermatol. Clin. 1993;11:709–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

