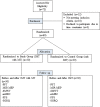
Effectiveness of 12-week inspiratory muscle training with manual therapy in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled study
- PMID: 35332685
- PMCID: PMC9060133
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.13486
Effectiveness of 12-week inspiratory muscle training with manual therapy in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled study
Abstract
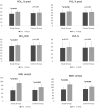
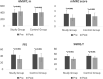
The benefits of inspiratory muscle training (IMT) in patients with COPD were reported. However, its effects are limited in severe COPD patients. Further researches are required in new and complementary modalities demonstrating IMT efficacy in severe COPD patients. This study aims to investigate effects of manual therapy (MT) additional over IMT on functional capacity, respiratory muscle strength, pulmonary function, dyspnea, fatigue, and quality of life in severe COPD patients. Sixty patients with COPD in GOLD stage III-IV were included in this prospective single-blind randomized trial. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either MT additional over IMT at 40% of maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) (n = 30) or only IMT (n = 30) for 12 weeks. MT group received MT during 12 weeks for 30 min additional to IMT. Pulmonary function, respiratory muscle strength, functional capacity, dyspnea, fatigue, and quality of life were evaluated by spirometry, mouth pressure device, six-minute walk test, Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea scale, fatigue severity scale, and St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), respectively. MT group had significantly greater improvement in FEV1%, FVC%, PEF%, respiratory muscle strength, function, dyspnea, fatigue, and quality of life compared with IMT group (p < 0.05). 6MWT (p < 0.001, effect size Cohen's d: 0.915), MIP (p < 0.001, effect size Cohen's d: 1.235), and mMRC score (p < 0.001, effect size Cohen's d: 0.982) were significantly improved in IMT with MT group. This study demonstrated that subjects in IMT with MT group had improved outcomes in functional capacity, respiratory muscle strength, pulmonary function, dyspnea, fatigue perception, and quality of life compared with alone IMT group.
Keywords: COPD; functional capacity; inspiratory muscle training; manual therapy.
© 2022 The Authors. The Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (2021). Retrieved September 19, 2018. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/GOLD-REPORT-2021-v1.1-25...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical