Development of a High-Throughput Screening Assay for Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Androgen Receptor Splice Variants
- PMID: 35333596
- PMCID: PMC9057896
- DOI: 10.1089/adt.2021.128
Development of a High-Throughput Screening Assay for Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Androgen Receptor Splice Variants
Abstract
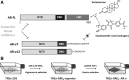
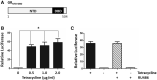
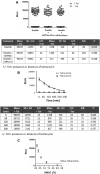
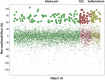
The role of the androgen receptor (AR) in the progression of prostate cancer (PCa) is well established and competitive inhibition of AR ligand binding domain (LBD) has been the mainstay of antiandrogen therapies for advanced and metastatic disease. However, the efficacy of such drugs is often limited by the emergence of resistance, mediated through point mutations and receptor splice variants lacking the AR-LBD. As a result, the prognosis for patients with malignant, castrate-resistant disease remains poor. The amino terminal domain (NTD) of the AR has been shown to be critical for AR function. Its modular activation function (AF-1) is important for both gene regulation and participation in protein-protein interactions. However, due to the intrinsically disordered structure of the domain, its potential as a candidate for therapeutic intervention has been generally overlooked. In this article, we describe the design and development of a functional cell-based assay aimed at identifying small-molecule inhibitors of the AR-NTD. We demonstrate the suitability of the assay for high-throughput screening platforms and validate two initial hits emerging from a small, targeted, library screen in PCa cells.
Keywords: AR-vs; androgen receptor; castrate-resistant prostate cancer; high-throughput screen; intrinsically disordered structure; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Globocan (2020). https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/27-Prostate-fact-sheet... (accessed February 28, 2022).
-
- Meng MV, Grossfeld GD, Sadetsky N, Mehta SS, Lubeck DP, Carroll PR: Contemporary patterns of androgen deprivation therapy use for newly diagnosed prostate cancer. Urology 2002;60(3 Suppl 1):7–11. - PubMed
-
- Scher HI, Sawyers CL: Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:8253–8261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

