C-type natriuretic peptide is a pivotal regulator of metabolic homeostasis
- PMID: 35333648
- PMCID: PMC9060477
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2116470119
C-type natriuretic peptide is a pivotal regulator of metabolic homeostasis
Abstract
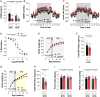
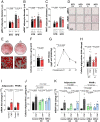
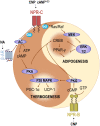
Thermogenesis and adipogenesis are tightly regulated mechanisms that maintain lipid homeostasis and energy balance; dysfunction of these critical processes underpins obesity and contributes to cardiometabolic disease. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) fulfills a multimodal protective role in the cardiovascular system governing local blood flow, angiogenesis, cardiac function, and immune cell reactivity. Herein, we investigated a parallel, preservative function for CNP in coordinating metabolic homeostasis. Global inducible CNP knockout mice exhibited reduced body weight, higher temperature, lower adiposity, and greater energy expenditure in vivo. This thermogenic phenotype was associated with increased expression of uncoupling protein-1 and preferential lipid utilization by mitochondria, a switch corroborated by a corresponding diminution of insulin secretion and glucose clearance. Complementary studies in isolated murine and human adipocytes revealed that CNP exerts these metabolic regulatory actions by inhibiting sympathetic thermogenic programming via Gi-coupled natriuretic peptide receptor (NPR)-C and reducing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α expression, while concomitantly driving adipogenesis via NPR-B/protein kinase-G. Finally, we identified an association between CNP/NPR-C expression and obesity in patient samples. These findings establish a pivotal physiological role for CNP as a metabolic switch to balance energy homeostasis. Pharmacological targeting of these receptors may offer therapeutic utility in the metabolic syndrome and related cardiovascular disorders.
Keywords: G protein–coupled receptor; adipogenesis; cardiometabolic disease; natriuretic peptide; thermogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a competing interest. A.J.H. is a scientific advisory board member/consultant for Palatin Technologies Inc. and Novo Nordisk, and has received research support from Palatin Technologies Inc. for an unrelated project.
Figures




References
-
- Eckel R. H., Obesity. Circulation 111, e257–e259 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Poirier P., et al. , American Heart Association; Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism, Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: An update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 113, 898–918 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Betz M. J., Enerbäck S., Targeting thermogenesis in brown fat and muscle to treat obesity and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 14, 77–87 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Špiranec K., et al. , Endothelial C-type natriuretic peptide acts on pericytes to regulate microcirculatory flow and blood pressure. Circulation 138, 494–508 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

