ISG15 deficiency restricts HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 35333911
- PMCID: PMC8986114
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010405
ISG15 deficiency restricts HIV-1 infection
Abstract
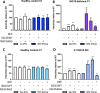
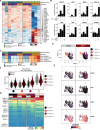
Type I interferons (IFN-Is) are a group of potent inflammatory and antiviral cytokines. They induce IFN stimulated genes (ISGs), which act as proinflammatory mediators, antiviral effectors, and negative regulators of the IFN-I signaling cascade itself. One such regulator is interferon stimulated gene 15 (ISG15). Humans with complete ISG15 deficiency express persistently elevated levels of ISGs, and consequently, exhibit broad spectrum resistance to viral infection. Here, we demonstrate that IFN-I primed fibroblasts derived from ISG15-deficient individuals are more resistant to infection with single-cycle HIV-1 compared to healthy control fibroblasts. Complementation with both wild-type (WT) ISG15 and ISG15ΔGG (incapable of ISGylation while retaining negative regulation activity) was sufficient to reverse this phenotype, restoring susceptibility to infection to levels comparable to WT cells. Furthermore, CRISPR-edited ISG15ko primary CD4+ T cells were less susceptible to HIV-1 infection compared to cells treated with non-targeting controls. Transcriptome analysis of these CRISPR-edited ISG15ko primary CD4+ T cells recapitulated the ISG signatures of ISG15 deficient patients. Taken together, we document that the increased broad-spectrum viral resistance in ISG15-deficiency also extends to HIV-1 and is driven by a combination of T-cell-specific ISGs, with both known and unknown functions, predicted to target HIV-1 replication at multiple steps.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: DB is founder and part owner of Lab11 Therapeutics Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Loeb KR, Haas AL. 1992. The IFN inducible 15-kDa ubiquitin homolog conjugates to intracellular proteins. J Biol Chem 267:7806–7813. - PubMed
-
- Haas AL, Ahrens P, Bright PM, Ankel H. 1987. Interferon induces a 15-ilodalton protein exhibiting marked homology to ubiquitin. J Biol Chem 262:11315–23. - PubMed
-
- Knight E, Cordova B. 1991. Ifn-Induced 15-Kda Protein Is Released from Human-Lymphocytes and Monocytes. Journal of Immunology 146:2280–2284. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

