Knockout of GGPPS1 restrains rab37-mediated autophagy in response to ventilator-induced lung injury
- PMID: 35334098
- PMCID: PMC8948466
- DOI: 10.1007/s13577-022-00692-7
Knockout of GGPPS1 restrains rab37-mediated autophagy in response to ventilator-induced lung injury
Abstract
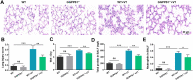
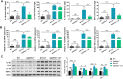
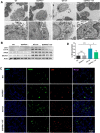
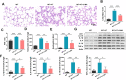
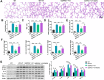
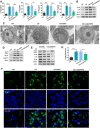
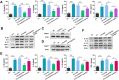
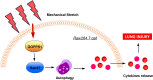
Mechanical ventilation may cause ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) in patients requiring ventilator support. Inhibition of autophagy is an important approach to ameliorate VILI as it always enhances lung injury after exposure to various stress agents. This study aimed to further reveal the potential mechanisms underlying the effects of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase large subunit 1 (GGPPS1) knockout and autophagy in VILI using C57BL/6 mice with lung-specific GGPPS1 knockout that were subjected to mechanical ventilation. The results demonstrate that GGPPS1 knockout mice exhibit significantly attenuated VILI based on the histologic score, the lung wet-to-dry ratio, total protein levels, neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines. Importantly, the expression levels of autophagy markers were obviously decreased in GGPPS1 knockout mice compared with wild-type mice. The inhibitory effects of GGPPS1 knockout on autophagy were further confirmed by measuring the ultrastructural change of lung tissues under transmission electron microscopy. In addition, knockdown of GGPPS1 in RAW264.7 cells reduced cyclic stretch-induced inflammation and autophagy. The benefits of GGPPS1 knockout for VILI can be partially eliminated through treatment with rapamycin. Further analysis revealed that Rab37 was significantly downregulated in GGPPS1 knockout mice after mechanical ventilation, while it was highly expressed in the control group. Simultaneously, Rab37 overexpression significantly enhances autophagy in cells that are treated with cyclin stretch, including GGPPS1 knockout cells. Collectively, our results indicate that GGPPS1 knockout results in reduced expression of Rab37 proteins, further restraining autophagy and VILI.
Keywords: Autophagy; GGPPS1; Inflammation; Rab37; Ventilator-induced lung injury.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Japan Human Cell Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest, financial or otherwise, is declared by the authors.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- (grant no. 81971726)/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- (grant no. BK20191351)/Natural science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- (grant no. 2020M670091ZX)/Postdoctoral Foundation of China
- (grant no. 2019k178)/Jiangsu Postdoctoral Research Fund
- (grant no. 2019JJ50021)/Hunan Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

