IL-3 Expands Pre-Basophil and Mast Cell Progenitors by Upregulating the IL-3 Receptor Expression
- PMID: 35334276
- PMCID: PMC9161734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2022.104498
IL-3 Expands Pre-Basophil and Mast Cell Progenitors by Upregulating the IL-3 Receptor Expression
Abstract
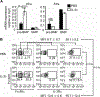
Basophils and mast cells play a critical role in allergic inflammation and provide protective immunity against certain types of parasitic infections. Expansion of basophils and mast cells to the critical numbers is believed to be an essential step in enabling basophils and mast cells to carry out their protective functions. However, factors that drive basophil and mast cell expansion are still incompletely understood. We tested the roles of cytokines and growth factors IL-3, TSLP, GM-CSF, IL-5, SCF, IL-7, IL-25, and IL-33 in promoting the differentiation of pre-basophil and mast cell progenitors (pre-BMPs)in vitro.We found that while GM-CSF only expanded basophils, IL-3 promoted the differentiation of pre-BMPs into both basophils and mast cells. We found that IL-3 expanded the number of pre-BMPsin vivo. We showed that IL-3 upregulatedIl3ramRNA and protein expression on pre-BMPs, supporting that IL-3 expands pre-BMPs in part by upregulating the IL-3 receptor expression. Although Gata2 mRNA expression was upregulated by IL-3 treatment in pre-BMPs, it is dispensable for IL-3-mediated upregulation of IL-3 receptor expression. Our study reveals a novel mechanism through which IL-3 expands basophil and mast cells.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


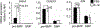
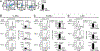
Similar articles
-
IL-3 induces basophil expansion in vivo by directing granulocyte-monocyte progenitors to differentiate into basophil lineage-restricted progenitors in the bone marrow and by increasing the number of basophil/mast cell progenitors in the spleen.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 1;182(5):2835-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802870. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19234178 Free PMC article.
-
Human interleukin-3 inhibits the binding of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-5 to basophils and strongly enhances their functional activity.J Cell Physiol. 1990 Oct;145(1):69-77. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450111. J Cell Physiol. 1990. PMID: 1698795
-
Effects of basophil-priming and stimulating cytokines on histamine release from isolated human skin mast cells.Arch Dermatol Res. 1996 Jul;288(8):463-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02505236. Arch Dermatol Res. 1996. PMID: 8844126
-
The role of basophils in allergic disease.Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996 Aug;22:126s-131s. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8871057 Review.
-
Hemopoietic growth factors regulate basophil function and viability.Immunol Ser. 1992;57:587-600. Immunol Ser. 1992. PMID: 1380308 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insights into the ontogeny of basophils.Front Allergy. 2024 May 13;5:1402841. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1402841. eCollection 2024. Front Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38803659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-Modulating Effects of Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Foods in Healthy Canines.Curr Dev Nutr. 2024 Feb 28;8(4):102128. doi: 10.1016/j.cdnut.2024.102128. eCollection 2024 Apr. Curr Dev Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38590952 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1 Induces Mucosal Mast Cell Genes and is Negatively Regulated by the IL-3/ERK1/2 Axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 11;23(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02048-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39934802 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin accessibility profiling of Treg cells in acute urticaria.Epigenetics. 2025 Dec;20(1):2503126. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2025.2503126. Epub 2025 May 12. Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40355834 Free PMC article.
-
The ontogenesis and heterogeneity of basophils.Discov Immunol. 2024 Feb 2;3(1):kyae003. doi: 10.1093/discim/kyae003. eCollection 2024. Discov Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38567293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Urban JF Jr., Schopf L, Morris SC, Orekhova T, Madden KB, Betts CJ, Gamble HR, Byrd C, Donaldson D, Else K, Finkelman FD, Stat6 signaling promotes protective immunity against Trichinella spiralis through a mast cell- and T cell-dependent mechanism, J Immunol, 164 (2000) 2046–2052. - PubMed
-
- Reitz M, Brunn ML, Rodewald HR, Feyerabend TB, Roers A, Dudeck A, Voehringer D, Jonsson F, Kuhl AA, Breloer M, Mucosal mast cells are indispensable for the timely termination of Strongyloides ratti infection, Mucosal immunology, 10 (2017) 481–492. - PubMed
-
- Lantz CS, Boesiger J, Song CH, Mach N, Kobayashi T, Mulligan RC, Nawa Y, Dranoff G, Galli SJ, Role for interleukin-3 in mast-cell and basophil development and in immunity to parasites, Nature, 392 (1998) 90–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

