In silico study of potential antiviral activity of copper(II) complexes with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on various SARS-CoV-2 target proteins
- PMID: 35334392
- PMCID: PMC8930182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2022.111805
In silico study of potential antiviral activity of copper(II) complexes with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on various SARS-CoV-2 target proteins
Abstract
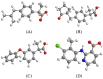
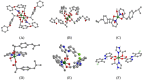
In silico molecular docking studies, in vitro toxicity and in silico predictions on the biological activity profile, pharmacokinetic properties, drug-likeness, ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) physicochemical pharmacokinetic data, and target proteins and toxicity predictions were performed on six copper(II) complexes with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ibuprofen, loxoprofen, fenoprofen and clonixin as ligands, in order to investigate the ability of these complexes to interact with the key therapeutic target proteins of SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2) 3C-like cysteine main protease (3CLpro/Mpro), viral papain-like protease (PLpro), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and non-structural proteins (Nsps) Nsp16-Nsp10 2'-O-methyltransferase complex, and their capacity to act as antiviral agents, contributing thus to understanding the role they can play in the context of coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Cytotoxic activity against five human cancer and normal cell lines were also evaluated.
Keywords: 3C–like cysteine main protease; Nsp16–Nsp10 2′–O–methyltransferase complex; Papain–like protease; RNA–dependent RNA polymerase; SARS–CoV–2 target proteins; in silico predictive tools.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
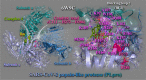

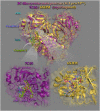



Similar articles
-
Black tea bioactives as inhibitors of multiple targets of SARS-CoV-2 (3CLpro, PLpro and RdRp): a virtual screening and molecular dynamic simulation study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Sep;40(15):7143-7166. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1897679. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33715595
-
Virtual screening, ADME/T, and binding free energy analysis of anti-viral, anti-protease, and anti-infectious compounds against NSP10/NSP16 methyltransferase and main protease of SARS CoV-2.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020 Dec;40(6):605-612. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1772298. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020. PMID: 32476594 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of FDA approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro), drug repurposing approach.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111544. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111544. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34311539 Free PMC article.
-
The SARS-coronavirus papain-like protease: structure, function and inhibition by designed antiviral compounds.Antiviral Res. 2015 Mar;115:21-38. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.12.015. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 25554382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonols as potential antiviral drugs targeting SARS-CoV-2 proteases (3CLpro and PLpro), spike protein, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and angiotensin-converting enzyme II receptor (ACE2).Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 15;891:173759. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173759. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33249077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Copper(II) and Cobalt(II) Complexes Based on Abietate Ligands from Pinus Resin: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;13(7):1202. doi: 10.3390/nano13071202. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37049296 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies Tackling Viral Replication and Inflammatory Pathways as Early Pharmacological Treatment for SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Any Potential Role for Ketoprofen Lysine Salt?Molecules. 2022 Dec 15;27(24):8919. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248919. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unusual Ni⋯Ni interaction in Ni(ii) complexes as potential inhibitors for the development of new anti-SARS-CoV-2 Omicron drugs.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Feb 20;15(3):895-915. doi: 10.1039/d3md00601h. eCollection 2024 Mar 20. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38516589 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-target activity of copper complexes: Antibacterial, DNA binding, and molecular docking with SARS-CoV-2 receptor.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Mar 1;373:110349. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110349. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36639010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malis G., Geromichalou E., Geromichalos G.D., Hatzidimitriou A.G., Psomas G. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021;224 - PubMed
-
- Jin Z., Du X., Xu Y., Deng Y., Liu M., Zhao Y., Zhang B., Li X., Zhang L., Peng C., Duan Y., Yu J., Wang L., Yang K., Liu F., Jiang R., Yang X., You T., Liu X., Yang X., Bai F., Liu H., Liu X., Guddat L., Xu W., Xiao G., Qin C., Shi Z., Jiang H., Rao Z., Yang-Show H. Nature. 2020;582:289–293. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

