Pigment epithelium-derived factor engineered to increase glycosaminoglycan affinity while maintaining bioactivity
- PMID: 35334413
- PMCID: PMC11371396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.03.079
Pigment epithelium-derived factor engineered to increase glycosaminoglycan affinity while maintaining bioactivity
Abstract
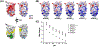
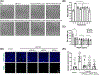
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is a secreted protein that is essential in tissue homeostasis and is involved in multiple functions in the eye, such as antiangiogenesis and neuroprotection. However, short retention in the retinal microenvironment can limit its therapeutic effects. In this study, we modified the amino acid sequence of PEDF to increase its affinity for heparin and hyaluronic acid (HA), which are negatively charged extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules. HA is the major component of the vitreous humor. We selectively converted neutral or anionic residues into cationic residues to obtain engineered PEDF (ePEDF). Using in vitro binding assays, we demonstrate that ePEDF had higher affinity for heparin and HA than wild-type PEDF (wtPEDF). ePEDF exhibited antiangiogenic and retinal survival bioactivities. It inhibited endothelial cell proliferation and tube formation in vitro. In an ex vivo model mimicking retinal degeneration, ePEDF protected photoreceptors from cell death. The findings suggest that protein engineering is an approach to develop active PEDF with higher ECM affinity to potentially improve its retention in the retina microenvironment and in turn make it a more efficient therapeutic drug for retinal diseases.
Keywords: Hyaluronic acid; Pigment epithelium-derived factor; Retinal disease.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Hunghao Chu and Yadong Wang are the shareholders of Ionic Biomedical Inc. Ivan T. Rebustini and S. Patricia Becerra declare no competing financial interests or personal relationships that influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures
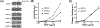
Similar articles
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor binds to hyaluronan. Mapping of a hyaluronan binding site.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 28;283(48):33310-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801287200. Epub 2008 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18805795 Free PMC article.
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) binds to glycosaminoglycans: analysis of the binding site.Biochemistry. 1998 Jul 28;37(30):10643-52. doi: 10.1021/bi9802317. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9692954
-
Mapping the type I collagen-binding site on pigment epithelium-derived factor. Implications for its antiangiogenic activity.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 22;277(47):45400-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208339200. Epub 2002 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12237317
-
Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor, a Protective Factor for Photoreceptors in Vivo.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;854:699-706. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-17121-0_93. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26427478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor regulation of neuronal and stem cell fate.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Apr 15;389(2):111891. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111891. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32035134 Review.
Cited by
-
PEDF and Its Role in Metabolic Disease, Angiogenesis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 21;13(7):1780. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071780. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- A Campochiaro P, Akhlaq A. Sustained suppression of VEGF for treatment of retinal/choroidal vascular diseases., Prog Retin Eye Res. 83 (2021) 100921. - PubMed
-
- Daien V, Eldem BM, Talks JS, Korobelnik J-F, Mitchell P, Finger RP, Sakamoto T, Wong TY, Evuarherhe O, Carter G, Carrasco J, Real-world data in retinal diseases treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapy - a systematic approach to identify and characterize data sources., BMC Ophthalmol. 19 (2019) 206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tombran-Tink J, Barnstable CJ, PEDF: a multifaceted neurotrophic factor., Nat. Rev. Neurosci 4 (2003) 628–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

