De Novo Detrusor Underactivity and Other Urodynamic Findings after Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35334557
- PMCID: PMC8949898
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58030381
De Novo Detrusor Underactivity and Other Urodynamic Findings after Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
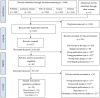
Background and objectives: The aim of this systematic review is to evaluate the impact of radical prostatectomy (RP) on bladder function, with special attention towards detrusor underactivity investigated with the means of urodynamic evaluation. Materials and Methods: The review was performed in accordance with the PRISMA statement and was registered in the PROSPERO (ID#: CRD42020223480). The studied population was limited to men with prostate cancer who underwent urodynamic study prior to and after radical prostatectomy. Eight hundred twenty-seven studies were screened, with twenty-five finally included. A qualitative analysis was performed. Rates of detrusor underactivity (DU) before surgery were reported in eight studies and ranged from 1.6% to 75% (median of 40.8%). DU occurred de novo after RP in 9.1% to 37% of patients (median of 29.1%). On the other hand, preexisting DU resolved in 7% to 35.5% of affected men. Detrusor overactivity (DO) was the most frequently reported outcome, being assessed in 23 studies. The rate of DO preoperatively was from 5% to 76% (median of 25%). De novo was reported in 2.3-54.4% of patients (median of 15%) and resolved after RP in 19.6% to 87.5% (median of 33%) of affected patients. Baseline rates of bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) varied between studies from 19% to 59.3%, with a median of 27.8%. The most pronounced change after surgery was the resolution of BOO in 88% to 93.8% (median of 92%) of affected patients. Results: Rates of de novo impaired bladder compliance (IBC) varied from 3.2% to 41.3% (median of 13.3%), whereas the resolution of IBC was reported with rates ranging from 0% to 47% (median of 4.8%). Conclusions: BOO, DO, and DU are frequently diagnosed in men scheduled for RP. BOO is improved after RP in most patients; however, there is still a substantial rate of patients with de novo DU as well as DO which may impair functional outcomes and quality of life.
Keywords: bladder outlet obstruction; detrusor overactivity; detrusor underactivity; impaired bladder compliance; radical prostatectomy; urodynamic study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cochetti G., Del Zingaro M., Ciarletti S., Paladini A., Felici G., Stivalini D., Cellini V., Mearini E. New Evolution of Robotic Radical Prostatectomy: A Single Center Experience with PERUSIA Technique. Appl. Sci. 2021;11:1513. doi: 10.3390/app11041513. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources