High-Resolution Separation of Nanoparticles Using a Negative Magnetophoretic Microfluidic System
- PMID: 35334669
- PMCID: PMC8951349
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13030377
High-Resolution Separation of Nanoparticles Using a Negative Magnetophoretic Microfluidic System
Abstract
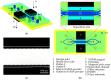
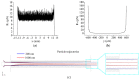
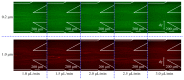
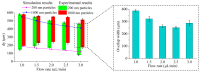
The separation and purification of a sample of interest is essential for subsequent detection and analysis procedures, but there is a lack of effective separation methods with which to purify nano-sized particles from the sample media. In this paper, a microfluidic system based on negative magnetophoresis is presented for the high-resolution separation of nanoparticles. The system includes on-chip magnetic pole arrays and permalloys that symmetrically distribute on both sides of the separation channel and four permanent magnets that provide strong magnetic fields. The microfluidic system can separate 200 nm particles with a high purity from the mixture (1000 nm and 200 nm particles) due to a magnetic field gradient as high as 10,000 T/m being generated inside the separation channel, which can provide a negative magnetophoretic force of up to 10 pN to the 1000 nm particle. The overall recovery rate of the particles reaches 99%, the recovery rate of 200 nm particles is 84.2%, and the purity reaches 98.2%. Compared with the existing negative magnetophoretic separation methods, our system not only exhibits high resolution on particle sizes (800 nm), but also improves the sample processing throughput, which reaches 2.5 μL/min. The microfluidic system is expected to provide a new solution for the high-purity separation of nanoparticles, as well as nanobiological samples.
Keywords: microfluidic chip; nanoparticles; negative magnetophoresis; separation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced microfluidic multi-target separation by positive and negative magnetophoresis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 10;14(1):13293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64330-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38858424 Free PMC article.
-
Label-free separation of nanoscale particles by an ultrahigh gradient magnetic field in a microfluidic device.Nanoscale. 2021 Feb 25;13(7):4029-4037. doi: 10.1039/d0nr08383f. Nanoscale. 2021. PMID: 33533377
-
Influence of magnetic convection on separation efficiency in magnetophoretic microfluidic processes: a combined simulation and experimental study.Nanoscale. 2025 Jan 16;17(3):1574-1584. doi: 10.1039/d4nr02225d. Nanoscale. 2025. PMID: 39628351
-
Magnetoanalysis of micro/nanoparticles: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Apr 1;690(2):137-47. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.019. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Anal Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 21435469 Review.
-
A Review on Magnetophoretic Immunoseparation.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016 Mar;16(3):2152-63. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2016.10930. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27455614 Review.
Cited by
-
Microplastic separation and enrichment in microchannels under derivative electric field gradient by bipolar electrode reactions.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 26;14(1):4626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54921-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38409340 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced microfluidic multi-target separation by positive and negative magnetophoresis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 10;14(1):13293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64330-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38858424 Free PMC article.
-
Optical sorting: past, present and future.Light Sci Appl. 2025 Feb 27;14(1):103. doi: 10.1038/s41377-024-01734-5. Light Sci Appl. 2025. PMID: 40011460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic nanoparticles fabricated/integrated with microfluidics for biological applications: A review.Biomed Microdevices. 2024 Jan 25;26(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s10544-023-00693-9. Biomed Microdevices. 2024. PMID: 38270676 Review.
-
Biomedical Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;12(11):1023. doi: 10.3390/bios12111023. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shen Y., Yalikun Y., Tanaka Y. Recent advances in microfluidic cell sorting systems. Sens. Actuators B. 2019;282:268–281. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.025. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 62074155/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019B020226004/Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province
- 2020A1515110938/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Provinc
- E1G049/SIAT Innovation Program for Excellent Young Researchers
- KCXFZ202002011008124/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

