Reversal of Doxorubicin-Induced Bone Loss and Mineralization by Supplementation of Resveratrol and MitoTEMPO in the Early Development of Sparus aurata
- PMID: 35334811
- PMCID: PMC8950850
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14061154
Reversal of Doxorubicin-Induced Bone Loss and Mineralization by Supplementation of Resveratrol and MitoTEMPO in the Early Development of Sparus aurata
Abstract
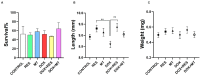
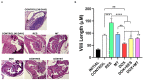
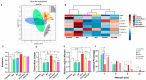
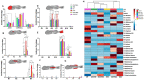
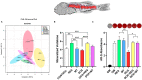
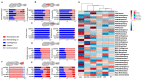
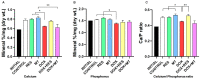
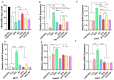
Doxorubicin is a widely used chemotherapeutic drug known to induce bone loss. The mechanism behind doxorubicin-mediated bone loss is unclear, but oxidative stress has been suggested as a potential cause. Antioxidants that can counteract the toxic effect of doxorubicin on the bone would be helpful for the prevention of secondary osteoporosis. We used resveratrol, a natural antioxidant, and MitoTEMPO, a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant, to counteract doxorubicin-induced bone loss and mineralization on Sparus aurata larvae. Doxorubicin supplemented Microdiets increased bone deformities, decreased mineralization, and lipid peroxidation, whereas Resveratrol and MitoTEMPO supplemented microdiets improved mineralization, decreased bone deformities, and reversed the effects of doxorubicin in vivo and in vitro, using osteoblastic VSa13 cells. Partial Least-Squares Discriminant Analysis highlighted differences between groups on the distribution of skeletal anomalies and mineralization of skeleton elements. Calcium and Phosphorus content was negatively affected in the doxorubicin supplemented group. Doxorubicin reduced the mRNA expression of antioxidant genes, including catalase, glutathione peroxidase 1, superoxide dismutase 1, and hsp90 suggesting that ROS are central for Doxorubicin-induced bone loss. The mRNA expression of antioxidant genes was significantly increased on resveratrol alone or combined treatment. The length of intestinal villi was increased in response to antioxidants and reduced on doxorubicin. Antioxidant supplements effectively prevent bone deformities and mineralization defects, increase antioxidant response and reverse doxorubicin-induced effects on bone anomalies, mineralization, and oxidative stress. A combined treatment of doxorubicin and antioxidants was beneficial in fish larvae and showed the potential for use in preventing Doxorubicin-induced bone impairment.
Keywords: MitoTEMPO; bone deformities; doxorubicin; mineralization; oxidative stress; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regular Supplementation with Antioxidants Rescues Doxorubicin-Induced Bone Deformities and Mineralization Delay in Zebrafish.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 23;14(23):4959. doi: 10.3390/nu14234959. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36500990 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary DHA and α-tocopherol on bone development, early mineralisation and oxidative stress in Sparus aurata (Linnaeus, 1758) larvae.Br J Nutr. 2013 May 28;109(10):1796-805. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512003935. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Br J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23046500
-
Dietary glutamine supplementation effects on amino acid metabolism, intestinal nutrient absorption capacity and antioxidant response of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) juveniles.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2016 Jan;191:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.09.012. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26424608
-
Effect of melatonin and folic acid supplementation on the growth performance, antioxidant status, and liver histology of the farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) under standard rearing conditions.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2020 Dec;46(6):2265-2280. doi: 10.1007/s10695-020-00879-5. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32978696
-
Therapeutic effect of resveratrol supplementation on oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Postgrad Med J. 2020 Apr;96(1134):197-205. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-136415. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Postgrad Med J. 2020. PMID: 31628212
Cited by
-
The osteogenic and mineralogenic potential of the microalgae Skeletonema costatum and Tetraselmis striata CTP4 in fish models.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Sep 30;80(10):310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04953-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37777592 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptotic- and non-ferroptotic mechanisms associated with doxorubicin-induced male reproductive dysfunction.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jun 4;14:102064. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.102064. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40548255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regular Supplementation with Antioxidants Rescues Doxorubicin-Induced Bone Deformities and Mineralization Delay in Zebrafish.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 23;14(23):4959. doi: 10.3390/nu14234959. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36500990 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Resveratrol and Apigenin on Jejunal Oxidative Injury in Ducks and on Immortalized Duck Intestinal Epithelial Cells Exposed to H2O2.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 17;13(5):611. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050611. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services Bone health and osteoporosis: A report of the Surgeon General. US Health Hum. Serv. 2004;437:NBK45513. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200932030-00004. - DOI
-
- Baek K.H., Oh K.W., Lee W.Y., Lee S.S., Kim M.K., Kwon H.S., Rhee E.J., Han J.H., Song K.H., Cha B.Y., et al. Association of oxidative stress with postmenopausal osteoporosis and the effects of hydrogen peroxide on osteoclast formation in human bone marrow cell cultures. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010;87:226–235. doi: 10.1007/s00223-010-9393-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

