Creatine Supplementation for Muscle Growth: A Scoping Review of Randomized Clinical Trials from 2012 to 2021
- PMID: 35334912
- PMCID: PMC8949037
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14061255
Creatine Supplementation for Muscle Growth: A Scoping Review of Randomized Clinical Trials from 2012 to 2021
Abstract
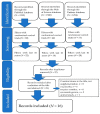
Creatine supplementation is the most popular ergonomic aid for athletes in recent years and is used for improving sport performance and muscle growth. However, creatine supplementation is not always effective in all populations. To address these discrepancies, numerous studies have examined the use of creatine supplementation for muscle growth. This scoping review aimed to investigate the effects of creatine supplementation for muscle growth in various populations, in which Arksey and O'Malley's scoping review framework is used to present the findings. For this study, we performed a systematic search of the PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases for theses and articles published between 2012 and 2021. A manual search of the reference lists of the uncovered studies was conducted and an expert panel was consulted. Two reviewers screened the articles for eligibility according to the inclusion criteria. Methodological quality was assessed using the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute's (NHLBI's) quality assessment tool. A total of 16 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were finally included. All the authors extracted key data and descriptively analyzed the data. Thematic analysis was used to categorize the results into themes. Three major themes related to muscle growth were generated: (i) subjects of creatine supplementation-muscle growth is more effective in healthy young subjects than others; (ii) training of subjects-sufficient training is important in all populations; (iii) future direction and recommendation of creatine supplementation for muscle growth-injury prevention and utilization in medical practice. Overall, creatine is an efficient form of supplementation for muscle growth in the healthy young population with adequate training in a variety of dosage strategies and athletic activities. However, more well-designed, long-term RCTs with larger sample sizes are needed in older and muscular disease-related populations to definitively determine the effects of creatine supplementation on muscle growth in these other populations.
Keywords: casting; ergogenic aids; older population; performance enhancement; sarcopenia; strength.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hartono F.A., Martin-Arrowsmith P.W., Peeters W.M., Churchward-Venne T.A. The Effects of Dietary Protein Supplementation on Acute Changes in Muscle Protein Synthesis and Longer-Term Changes in Muscle Mass, Strength, and Aerobic Capacity in Response to Concurrent Resistance and Endurance Exercise in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2022 doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01620-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical