Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Immune Responses Up to Six Months Following Homologous or Heterologous Primary Immunization with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccines
- PMID: 35334989
- PMCID: PMC8953845
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10030359
Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Immune Responses Up to Six Months Following Homologous or Heterologous Primary Immunization with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccines
Abstract
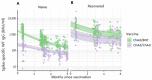
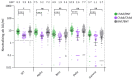
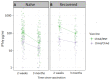
Heterologous primary immunization against SARS-CoV-2 is part of applied recommendations. However, little is known about duration of immune responses after heterologous vaccine regimens. To evaluate duration of immune responses after primary vaccination with homologous adeno-vectored ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (ChAd) or heterologous ChAd/BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine (BNT), anti-spike-IgG and SARS-CoV-2 VOC-neutralizing antibody responses were measured in 354 healthcare workers (HCW) at 2 weeks, 3 months, 5 months and 6 months after the second vaccine dose. T-cell responses were investigated using a whole blood interferon gamma (IFN-γ) release assay 2 weeks and 3 months post second vaccine dose. Two hundred and ten HCW immunized with homologous BNT were enrolled for comparison of antibody responses. In study participants naïve to SARS-CoV-2 prior to vaccination, heterologous ChAd/BNT resulted in 6-fold higher peak anti-spike IgG antibody titers compared to homologous ChAd vaccination. The half-life of antibody titers was 3.1 months (95% CI 2.8-3.6) following homologous ChAd vaccination and 1.9 months (95% CI 1.7-2.1) after heterologous vaccination, reducing the GMT difference between the groups to 3-fold 6 months post vaccination. Peak T-cell responses were stronger in ChAd/BNT vaccinees, but no significant difference was observed 3 months post vaccination. SARS-CoV-2 infection prior to vaccination resulted in substantially higher peak GMTs and IFN-γ levels and enhanced SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody and T cell responses over time. Heterologous primary SARS-CoV-2 immunization with ChAd and BNT elicits a stronger initial immune response compared to homologous vaccination with ChAd. However, although the differences in humoral responses remain over 6 months, the difference in SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell responses are no longer significant three months after vaccination.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2 vaccination; T-cells; antibodies; duration; heterologous; humoral response; immune response; immunity; immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Hober has participated on Astra Zeneca COVID-19 SCG Virtual Advisory Board.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Humoral immunogenicity and tolerability of heterologous ChAd/BNT compared with homologous BNT/BNT and ChAd/ChAd SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in hemodialysis patients : A multicenter prospective observational study.J Nephrol. 2022 Jun;35(5):1467-1478. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01247-7. Epub 2022 Jan 27. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35084719 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of humoral and cellular immune activation up to 21 months after heterologous and homologous COVID-19 vaccination.Front Immunol. 2025 May 2;16:1579163. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1579163. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40386778 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of humoral and cellular immune responses between ChAd-BNT heterologous vaccination and BNT-BNT homologous vaccination following the third BNT dose: A prospective cohort study.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1120556. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1120556. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36936965 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of heterologous versus homologous prime-boost schedules with an adenoviral vectored and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: a systematic review.Infect Dis Poverty. 2022 May 13;11(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40249-022-00977-x. Infect Dis Poverty. 2022. PMID: 35562753 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and neutralizing antibody levels and vaccine efficacy/effectiveness compared between heterologous and homologous primary series COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2022 Dec;40(4):321-336. doi: 10.12932/AP-121122-1501. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36681658
Cited by
-
Severe Breakthrough COVID-19 Cases during Six Months of Delta Variant (B.1.617.2) Domination in Poland.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Apr 4;10(4):557. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10040557. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455306 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of an RBD-nucleocapsid fusion protein as a booster candidate for COVID-19 vaccine.iScience. 2024 Jun 4;27(7):110177. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110177. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38993669 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in BNT126b2 and ChAdOx1 Homologous Vaccination Antibody Response among Teachers in Poznan, Poland.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;11(1):118. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11010118. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679962 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Persistence and Safety After SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b1 mRNA Vaccination in Chinese Adults: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Phase 1 Trial.Adv Ther. 2022 Aug;39(8):3789-3798. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02206-1. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35771353 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity and Durability of Antibody Responses to Homologous and Heterologous Vaccinations with BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 Vaccines for COVID-19.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 4;10(11):1864. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111864. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borobia A.M., Carcas A.J., Pérez-Olmeda M., Castaño L., Bertran M.J., García-Pérez J., Campins M., Portolés A., González-Pérez M., Morales M.T.G., et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of BNT162b2 booster in ChAdOx1-S-primed participants (CombiVacS): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2021;398:121–130. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01420-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barros-Martins J., Hammerschmidt S.I., Cossmann A., Odak I., Stankov M.V., Ramos G.M., Dopfer-Jablonka A., Heidemann A., Ritter C., Friedrichsen M., et al. Immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants after heterologous and homologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/BNT162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2021;27:1525–1529. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01449-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dimeglio C., Herin F., Da-Silva I., Jougla I., Pradere C., Porcheron M., Martin-Blondel G., Chapuy-Regaud S., Izopet J. Heterologous ChAdOx1-S/BNT162b2 Vaccination: Neutralizing Antibody Response to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021:ciab705. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hillus D., Schwarz T., Tober-Lau P., Vanshylla K., Hastor H., Thibeault C., Jentzsch S., Helbig E.T., Lippert L.J., Tscheak P., et al. Safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of homologous and heterologous prime-boost immunisation with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021;9:1255–1265. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00357-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

