IMGT® Biocuration and Analysis of the Rhesus Monkey IG Loci
- PMID: 35335026
- PMCID: PMC8950363
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10030394
IMGT® Biocuration and Analysis of the Rhesus Monkey IG Loci
Abstract
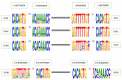
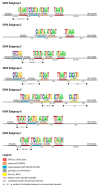
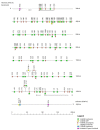
The adaptive immune system, along with the innate immune system, are the two main biological processes that protect an organism from pathogens. The adaptive immune system is characterized by the specificity and extreme diversity of its antigen receptors. These antigen receptors are the immunoglobulins (IG) or antibodies of the B cells and the T cell receptors (TR) of the T cells. The IG are proteins that have a dual role in immunity: they recognize antigens and trigger elimination mechanisms, to rid the body of foreign cells. The synthesis of the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains requires gene rearrangements at the DNA level in the IGH, IGK, and IGL loci. The rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) is one of the most widely used nonhuman primate species in biomedical research. In this manuscript, we provide a thorough analysis of the three IG loci of the Mmul_10 assembly of rhesus monkey, integrating IMGT previously existing data. Detailed characterization of IG genes includes their localization and position in the loci, the determination of the allele functionality, and the description of the regulatory elements of their promoters as well as the sequences of the conventional recombination signals (RS). This complete annotation of the genomic IG loci of Mmul_10 assembly and the highly detailed IG gene characterization could be used as a model, in additional rhesus monkey assemblies, for the analysis of the IG allelic polymorphism and structural variation, which have been described in rhesus monkeys.
Keywords: IGH locus; IGK locus; IGL locus; IMGT; Macaca mulatta; immunogenetics; immunoglobulins; immunoinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
From IMGT-ONTOLOGY to IMGT/LIGMotif: the IMGT standardized approach for immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene identification and description in large genomic sequences.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Apr 30;11:223. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-223. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20433708 Free PMC article.
-
IG and TR single chain fragment variable (scFv) sequence analysis: a new advanced functionality of IMGT/V-QUEST and IMGT/HighV-QUEST.BMC Immunol. 2017 Jun 26;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12865-017-0218-8. BMC Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28651553 Free PMC article.
-
IMGT® Biocuration and Comparative Study of the T Cell Receptor Beta Locus of Veterinary Species Based on Homo sapiens TRB.Front Immunol. 2020 May 5;11:821. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00821. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32431713 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulins or Antibodies: IMGT® Bridging Genes, Structures and Functions.Biomedicines. 2020 Aug 31;8(9):319. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8090319. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32878258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody Informatics: IMGT, the International ImMunoGeneTics Information System.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Apr;2(2). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.AID-0001-2012. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26105823 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering Gorilla gorilla gorilla immunoglobulin loci in multiple genome assemblies and enrichment of IMGT resources.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1475003. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1475003. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450182 Free PMC article.
-
Development of ferret immune repertoire reference resources and single-cell-based high-throughput profiling assays.J Virol. 2025 Apr 15;99(4):e0018125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00181-25. Epub 2025 Mar 21. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40116504 Free PMC article.
-
Novel rhesus macaque immunoglobulin germline genes identified by three sequencing approaches.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1506348. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1506348. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39776901 Free PMC article.
-
Digger: directed annotation of immunoglobulin and T cell receptor V, D, and J gene sequences and assemblies.Bioinformatics. 2024 Mar 4;40(3):btae144. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae144. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38478393 Free PMC article.
-
Guiding HIV-1 vaccine development with preclinical nonhuman primate research.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023 Nov 1;18(6):315-322. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000819. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023. PMID: 37712825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lefranc M.-P., Lefranc G. The Immunoglobulin FactsBook. Academic Press; London, UK: 2001.
-
- Lefranc M.-P., Lefranc G. The T Cell Receptor FactsBook. Academic Press; London, UK: 2001.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

