COVID-19 Vaccines and Hyperglycemia-Is There a Need for Postvaccination Surveillance?
- PMID: 35335086
- PMCID: PMC8952286
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10030454
COVID-19 Vaccines and Hyperglycemia-Is There a Need for Postvaccination Surveillance?
Abstract
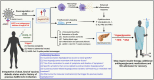
The COVID-19 vaccines currently in use have undoubtedly played the most significant role in combating the SARS-CoV-2 virus and reducing disease severity and the risk of death among those affected, especially among those with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes. The management of blood glucose levels has become critical in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, where data show two- to threefold higher intensive care hospital admissions and more than twice the mortality rate among diabetic COVID-19 patients when compared with their nondiabetic counterparts. Furthermore, new-onset diabetes and severe hyperglycemia-related complications, such as hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), were reported in COVID-19 patients. However, irrespective of the kind of vaccine and dosage number, possible vaccination-induced hyperglycemia and associated complications were reported among vaccinated individuals. The current article summarizes the available case reports on COVID-19 vaccination-induced hyperglycemia, the possible molecular mechanism responsible for this phenomenon, and the outstanding questions that need to be addressed and discusses the need to identify at-risk individuals and promote postvaccination monitoring/surveillance among at-risk individuals.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2; diabetes; diabetic ketoacidosis; hyperglycemia; hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- JHU Coronavirus Resource Center. 2022. [(accessed on 6 March 2022)]. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- WHO Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. 2021. [(accessed on 15 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.....
-
- WHO Update on Omicron. 2021. [(accessed on 15 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2021-update-on-omicron.
-
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Vaccines Safety. 2021. [(accessed on 16 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-dis....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

