Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Marine-Derived Fungus Emericellopsis sp. SCSIO41202
- PMID: 35335187
- PMCID: PMC8948984
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27061823
Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Marine-Derived Fungus Emericellopsis sp. SCSIO41202
Abstract
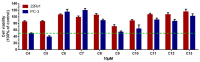
Two undescribed cytochalasins, emeriglobosins A (1) and B (2), together with nine previously reported analogues (3-11) and two known tetramic acid derivatives (12, 13) were isolated from the solid culture of Emericellopsis sp. SCSIO41202. Their structures, including the absolute configurations of their stereogenic carbons, were fully elucidated based on spectroscopic analysis and the calculated ECD. Some of the isolated compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxicity and enzyme inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in vitro. Among them, 8 showed potent AChE inhibitory activity, with an IC50 value of 1.31 μM, and 5 showed significant cytotoxicity against PC-3 cells, with an IC50 value of 2.32 μM.
Keywords: Emericellopsis sp.; chaetoglobosins; emeriglobosin; marine-derived fungus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Tran Hong Q., Nguyen Viet P., Tran Thi Hong H., Nguyen Xuan C., Nguyen Thi Thanh N., Oh H., Nguyen Hoai N., Chau Van M. Cytotoxic and immunomodulatory phenol derivatives from a marine sponge-derived fungus Ascomycota sp. VK12. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021;35:5153–5159. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZDKJ202018/Finance Science and Technology Project of Hainan Province
- GML2019ZD0406/Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)
- 21977102, 81860626, 81973235/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019BT02Y262/Guangdong Local Innovation Team Program
- [2020]039/Special Funds for Promoting Economic Development (Marine Economic Development) of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

