Novel Thymoquinone Nanoparticles Using Poly(ester amide) Based on L-Arginine-Targeting Pulmonary Drug Delivery
- PMID: 35335412
- PMCID: PMC8956027
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14061082
Novel Thymoquinone Nanoparticles Using Poly(ester amide) Based on L-Arginine-Targeting Pulmonary Drug Delivery
Abstract
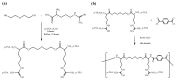
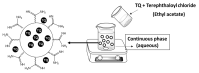
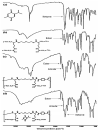
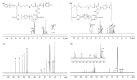
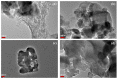
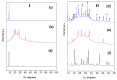
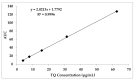
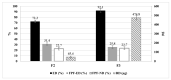
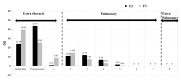
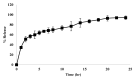
Thymoquinone (TQ), the main active constituent of Nigella sativa, has demonstrated broad-spectrum antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, which suggest its potential use in secondary infections caused by COVID-19. However, clinical deployment has been hindered due to its limited aqueous solubility and poor bioavailability. Therefore, a targeted delivery system to the lungs using nanotechnology is needed to overcome limitations encountered with TQ. In this project, a novel TQ-loaded poly(ester amide) based on L-arginine nanoparticles was prepared using the interfacial polycondensation method for a dry powder inhaler targeting delivery of TQ to the lungs. The nanoparticles were characterized by FTIR and NMR to confirm the structure. Transmission electron microscopy and Zetasizer results confirmed the particle diameter of 52 nm. The high-dose formulation showed the entrapment efficiency and loading capacity values of TQ to be 99.77% and 35.56%, respectively. An XRD study proved that TQ did not change its crystallinity, which was further confirmed by the DSC study. Optimized nanoparticles were evaluated for their in vitro aerodynamic performance, which demonstrated an effective delivery of 22.7-23.7% of the nominal dose into the lower parts of the lungs. The high drug-targeting potential and efficiency demonstrates the significant role of the TQ nanoparticles for potential application in COVID-19 and other respiratory conditions.
Keywords: COVID-19; L-arginine; nanoparticles; poly(ester amide); respiratory drug delivery; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and Characterization of Transdermal Patches Using Novel Thymoquinone-L-Arginine-Based Polyamide Nanocapsules for Potential Use in the Management of Psoriasis.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Mar 27;25(4):69. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02781-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38538972
-
The Influence of Pluronic F68 and F127 Nanocarrier on Physicochemical Properties, In vitro Release, and Antiproliferative Activity of Thymoquinone Drug.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;9(1):12-20. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.199774. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28250648 Free PMC article.
-
Development and biological evaluation of protective effect of kidney targeted N-acetylated chitosan nanoparticles containing thymoquinone for the treatment of DNA damage in cyclophosphamide-induced haemorrhagic cystitis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Aug 1;214:391-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.070. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35714868
-
Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jul 27;16:5117-5131. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S314321. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34349511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocarriers: more than tour de force for thymoquinone.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Apr;17(4):479-494. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1730808. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32077770 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Characterization of Transdermal Patches Using Novel Thymoquinone-L-Arginine-Based Polyamide Nanocapsules for Potential Use in the Management of Psoriasis.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Mar 27;25(4):69. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02781-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38538972
-
Taste Masking of Promethazine Hydrochloride Using l-Arginine Polyamide-Based Nanocapsules.Molecules. 2023 Jan 11;28(2):748. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020748. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677806 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation of Thymoquinone Nanoparticles to Semen Extender Boosts Cryotolerance and Fertilizing Ability of Buffalo Bull Spermatozoa.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 20;13(18):2973. doi: 10.3390/ani13182973. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760374 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of lung diseases via nanoparticles and nanorobots: Are these viable alternatives to overcome current treatments?Mater Today Bio. 2025 Feb 26;31:101616. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101616. eCollection 2025 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40124344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary inhalation for disease treatment: Basic research and clinical translations.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Jan 22;25:100966. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100966. eCollection 2024 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38318475 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Naser A.Y., Dahmash E.Z., Al-Rousan R., Alwafi H., Alrawashdeh H.M., Ghoul I., Abidine A., Bokhary M.A., AL-Hadithi H.T., Ali D., et al. Mental Health Status of the General Population, Healthcare Professionals, and University Students during 2019 Coronavirus Disease Outbreak in Jordan: A Cross-Sectional Study. Brain Behav. 2020;10:e01730. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Younus M.A.K., Younus H. Potential Implications of Black Seed and Its Principal Constituent Thymoquinone in the Treatment of COVID-19 Patients. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021;22:1315–1324. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

