Mucoadhesive Buccal Film of Estradiol for Hormonal Replacement Therapy: Development and In-Vivo Performance Prediction
- PMID: 35335917
- PMCID: PMC8955147
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030542
Mucoadhesive Buccal Film of Estradiol for Hormonal Replacement Therapy: Development and In-Vivo Performance Prediction
Abstract
The age-related loss of circulating estrogen that occurs during the menopausal transition manifests itself through a variety of symptoms including vasomotor (hot flushes and night sweats), genito-urinary syndrome (vaginal dryness and urinary symptoms), sexual dysfunction, mood, and sleep disturbance that often last longer than a decade. Furthermore, reductions in estrogen level increase the risks of chronic complications such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and cognitive decline among others, thereby affecting the quality of life of women. Although oral estrogens are the most widely used therapy for menopausal symptoms, they suffer from poor bioavailability, and there are concerns over their safety, creating a significant concern to consumers. Mucoadhesive buccal films are an innovative dosage form that offers several advantages including avoidance of the first-pass metabolism, fast onset of action, and importantly, improved patient acceptance. In the current work, we developed mucoadhesive estradiol film for hormonal replacement therapy using film-forming polymers. Two approaches, namely, co-solvency and nano-emulsion were evaluated to increase solubility and hence incorporate estradiol, a poorly water-soluble drug, into a formulation made from the hydrophilic polymer/s. The films were characterised for their mechanical and physicochemical properties. In-vitro release study showed that about 80% of the drug was released within 6 min from films prepared by the nano-emulsion approach, whereas it took about 10.5 min to get similar drug release from films prepared by the co-solvency approach. The ex-vivo permeation result indicates that about 15% of the drug permeated across the porcine buccal mucosa in the first 10 h from films prepared by the nano-emulsion approach, while permeation across porcine buccal mucosa was only observed at around 24 h from films prepared by the co-solvency method. The nano-emulsion films were evaluated for in vivo performance using a convolution technique using R software. The predicted Cmax and Tmax were found to be 740.74 ng mL-1 and 7 min, respectively, which were higher than previously reported in vivo concentration from oral tablets. The results demonstrated that mucoadhesive film of estradiol based on the nano-emulsion approach could be a promising platform for the delivery of estradiol through the buccal mucosa for the treatment of menopausal symptoms.
Keywords: estradiol; film; in vivo prediction; menopause; mucoadhesive; patient-centric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
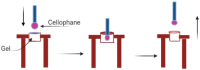





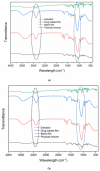


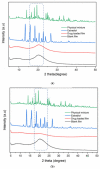

Similar articles
-
3D printed bilayer mucoadhesive buccal film of estradiol: Impact of design on film properties, release kinetics and predicted in vivo performance.Int J Pharm. 2022 Nov 25;628:122324. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122324. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 36280219
-
Enhancement of Simvastatin ex vivo Permeation from Mucoadhesive Buccal Films Loaded with Dual Drug Release Carriers.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jun 9;15:4001-4020. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S256925. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32606661 Free PMC article.
-
New formulation and approach for mucoadhesive buccal film of rizatriptan benzoate.Prog Biomater. 2017 Dec;6(4):175-187. doi: 10.1007/s40204-017-0077-7. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Prog Biomater. 2017. PMID: 29110144 Free PMC article.
-
Buccal films: A review of therapeutic opportunities, formulations & relevant evaluation approaches.J Control Release. 2022 Dec;352:1071-1092. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.058. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36351519 Review.
-
Manufacture and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal films.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011 Feb;77(2):187-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.11.023. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011. PMID: 21130875 Review.
Cited by
-
A review on lipid and polymeric nano-based 17-β-estradiol delivery systems: advances and challenges.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2024 Nov 15;27:13633. doi: 10.3389/jpps.2024.13633. eCollection 2024. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39619127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excipients in Pharmaceutical Additive Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Exploration of Polymeric Material Selection for Enhanced 3D Printing.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 24;16(3):317. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030317. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38543211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formulation and Characterization of Buccal Films Containing Valsartan with Additional Support from Image Analysis.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Mar 3;24(3):72. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02537-4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 36869211
-
Development and Optimization of Imiquimod-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Using a Hybrid Design of Experiments Approach.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Feb 22;18:1007-1029. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S400610. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36855538 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Characterisation of a Mucoadhesive Buccal Film Loaded with Doxycycline Hyclate for Topical Application in Periodontitis.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 8;15(2):580. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020580. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleat-Surgeou Corry R.N.X., Rooney R. The Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. [(accessed on 20 January 2022)]. Available online: https://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC2434947&blobtype....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

