Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application
- PMID: 35335920
- PMCID: PMC8955843
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030543
Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application
Abstract
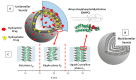
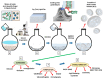
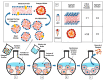
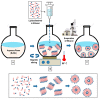
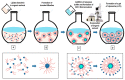
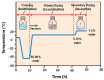
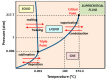
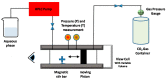
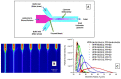
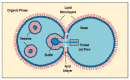
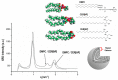
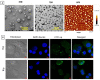
Liposomes are nano-sized spherical vesicles composed of an aqueous core surrounded by one (or more) phospholipid bilayer shells. Owing to their high biocompatibility, chemical composition variability, and ease of preparation, as well as their large variety of structural properties, liposomes have been employed in a large variety of nanomedicine and biomedical applications, including nanocarriers for drug delivery, in nutraceutical fields, for immunoassays, clinical diagnostics, tissue engineering, and theranostics formulations. Particularly important is the role of liposomes in drug-delivery applications, as they improve the performance of the encapsulated drugs, reducing side effects and toxicity by enhancing its in vitro- and in vivo-controlled delivery and activity. These applications stimulated a great effort for the scale-up of the formation processes in view of suitable industrial development. Despite the improvements of conventional approaches and the development of novel routes of liposome preparation, their intrinsic sensitivity to mechanical and chemical actions is responsible for some critical issues connected with a limited colloidal stability and reduced entrapment efficiency of cargo molecules. This article analyzes the main features of the formation and fabrication techniques of liposome nanocarriers, with a special focus on the structure, parameters, and the critical factors that influence the development of a suitable and stable formulation. Recent developments and new methods for liposome preparation are also discussed, with the objective of updating the reader and providing future directions for research and development.
Keywords: drug delivery; lipid-based nanocarriers; liposome formation; nanomedicine; phospholipids self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

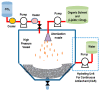
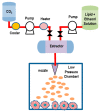
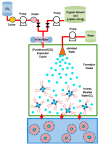
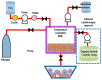

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

