Surface-Modified Bilosomes Nanogel Bearing a Natural Plant Alkaloid for Safe Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation
- PMID: 35335939
- PMCID: PMC8951435
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030563
Surface-Modified Bilosomes Nanogel Bearing a Natural Plant Alkaloid for Safe Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation
Abstract
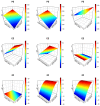
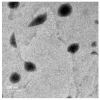
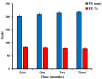
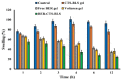
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory illness affecting the joints. The characteristic of RA is gradual joint deterioration. Current RA treatment alleviates signs such as inflammation and pain and substantially slows the progression of the disease. In this study, we aimed to boost the transdermal delivery of berberine (a natural product) by encapsulating it in chitosan, surface-modified bilosomes nanogel for better management of the inflammation of RA. The chitosan-coated bilosomes loaded with berberine (BER-CTS-BLS) were formulated according to the thin-film hydration approach and optimized for various causal variables, considering the effect of lipid, sodium deoxycholate, and chitosan concentrations on the size of the particles, entrapment, and the surface charge. The optimized BER-CTS-BLS has 202.3 nm mean diameter, 83.8% entrapment, and 30.8 mV surface charge. The optimized BER-CTS-BLS exhibited a delayed-release profile in vitro and increased skin permeability ex vivo. Additionally, histological examination revealed that the formulated BLS had no irritating effects on the skin. Furthermore, the optimized BER-CTS-BLS ability to reduce inflammation was evaluated in rats with carrageenan-induced paw edema. Our results demonstrate that the group treated with topical BER-CTS-BLS gel exhibited a dramatic reduction in rat paw edema swelling percentage to reach 24.4% after 12 h, which was substantially lower than other groups. Collectively, chitosan-coated bilosomes containing berberine have emerged as a promising therapeutic approach to control RA inflammation.
Keywords: berberine; bilosomes; carrageenan-induced paw edema; chitosan; inflammation; nanogel; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel nanogel loaded with chitosan decorated bilosomes for transdermal delivery of terbutaline sulfate: artificial neural network optimization, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020 Apr;10(2):471-485. doi: 10.1007/s13346-019-00688-1. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 31677149
-
Bilosomes as a promising nanoplatform for oral delivery of an alkaloid nutraceutical: improved pharmacokinetic profile and snowballed hypoglycemic effect in diabetic rats.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2694-2704. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2110997. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35975320 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanocarriers Overlaid with Chitosan for Brain Delivery of Berberine via the Nasal Route.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Feb 24;15(3):281. doi: 10.3390/ph15030281. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337079 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of berberine in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: From multiple targets to therapeutic potential.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jul;169:105667. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105667. Epub 2021 May 11. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33989762 Review.
-
Potential of Berberine for Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention and Treatment.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 May 14. doi: 10.1007/s11655-025-4217-y. Online ahead of print. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 40366564 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Novel Vesicular Bilosomal Delivery Systems for Dermal/Transdermal Applications.Curr Drug Deliv. 2024;21(7):961-977. doi: 10.2174/1567201820666230707161206. Curr Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 37424346 Review.
-
Surface Modification of Lipid-Based Nanocarriers: A Potential Approach to Enhance Targeted Drug Delivery.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 20;8(1):74-86. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05976. eCollection 2023 Jan 10. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36643539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal Nanotransferosomal Gel for Quercetin Brain Targeting: I. Optimization, Characterization, Brain Localization, and Cytotoxic Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 23;15(7):1805. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071805. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37513991 Free PMC article.
-
Triterpenes Drug Delivery Systems, a Modern Approach for Arthritis Targeted Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 28;17(1):54. doi: 10.3390/ph17010054. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polysaccharide-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 14;15(5):602. doi: 10.3390/ph15050602. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

