Pharmacokinetics of Curative Tranexamic Acid in Parturients Undergoing Cesarean Delivery
- PMID: 35335955
- PMCID: PMC8952437
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030578
Pharmacokinetics of Curative Tranexamic Acid in Parturients Undergoing Cesarean Delivery
Abstract
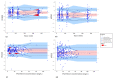
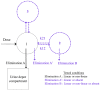
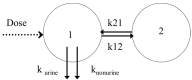
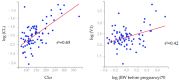
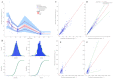
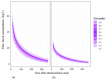
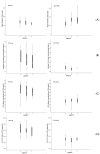
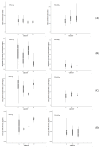
The aim of this study was to evaluate the population pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid (TXA) administered intravenously at a single dose of 0.5 or 1 g in parturients undergoing active hemorrhagic cesarean delivery and to evaluate the influence of patient variables on TXA pharmacokinetics. Subjects from three recruiting centers were included in this PK sub-study if randomized in the experimental group (i.v TXA 0.5 g or 1 g over one minute) of the TRACES study. Blood samples and two urinary samples were collected within 6 h after TXA injection. Parametric non-linear mixed-effect modeling (Monolix v2020R1) was computed. The final covariate model building used 315 blood and 117 urinary concentrations from seventy-nine patients. A two-compartment model with a double first-order elimination from the central compartment best described the data. The population estimates of clearance (CL), central volume of distribution (V1), and half-life for a typical 70 kg patient with an estimated renal clearance of 150 mL/min (Cockroft-Gault) were 0.14 L/h, 9.25 L, and 1.8 h. A correlation between estimated creatinine clearance and CL, body weight before pregnancy, and V1 was found and partly explained the PK variability. The final model was internally validated using a 500-run bootstrap. The first population pharmacokinetic model of TXA in active hemorrhagic caesarean section was successfully developed and internally validated.
Keywords: caesarean section; intravenous; pharmacokinetics; postpartum hemorrhage; tranexamic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Kassebaum N.J., Barber R.M., Bhutta Z.A., Dandona L., Gething P.W., Hay S.I., Kinfu Y., Larson H.J., Liang X., Lim S.S., et al. Global, regional, and national levels of maternal mortality, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1775–1812. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31470-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

