mRNA Lipoplexes with Cationic and Ionizable α-Amino-lipophosphonates: Membrane Fusion, Transfection, mRNA Translation and Conformation
- PMID: 35335957
- PMCID: PMC8952827
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030581
mRNA Lipoplexes with Cationic and Ionizable α-Amino-lipophosphonates: Membrane Fusion, Transfection, mRNA Translation and Conformation
Abstract
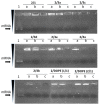
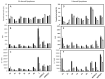
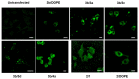
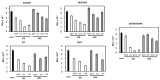
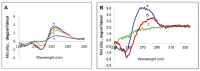
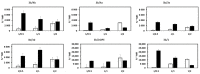
Cationic liposomes are attractive carriers for mRNA delivery. Here, mRNA lipoplexes (LX) were prepared with the cationic lipids α-aminolipophosphonate (3b) or imidazolium lipophosphoramidate (2) associated with various α-aminolipophosphonates co-lipids comprising protonable groups (imidazole or pyridine) and DOPE. Physicochemical parameters of liposomes and their membrane fusion activity were measured. LXs comprising either 3b- or 2- allowed transfection of ~25% and 40% of dendritic cells with low cytotoxicity, respectively; the efficiency increased up to 80% when 2 was combined with the imidazole-based co-lipid 1. The transfections were high with 3b/1, 3b/DOPE, 2/1 and 2/DOPE LXs. We observed that the transfection level was not well correlated with the acid-mediated membrane fusion activity of liposomes supposed to destabilize endosomes. The mRNA release from LXs and its translation capacity after release were studied for the most efficient LXs. The results showed that the more mRNA was condensed, the poorer the translation efficiency after release was. In contrast to DNA, circular dichroism performed on mRNA complexed with 2/DOPE revealed the presence of denatured mRNA in LXs explaining this lack of translation efficiency. This is an important parameter that should be stressed for the preparation of mRNA LXs with a conserved mRNA translation activity.
Keywords: cationic liposomes; dendritic cells; imidazolium lipophosphoramidate; lipoplexes; mRNA transfection; α-aminolipophosphonate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis of α-amino-lipophosphonates as cationic lipids or co-lipids for DNA transfection in dendritic cells.J Mater Chem B. 2017 Sep 7;5(33):6869-6881. doi: 10.1039/c7tb01080j. Epub 2017 Aug 4. J Mater Chem B. 2017. PMID: 32264336
-
Synthesis and transfection activity of new cationic phosphoramidate lipids: high efficiency of an imidazolium derivative.Chembiochem. 2008 Jun 16;9(9):1462-71. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700727. Chembiochem. 2008. PMID: 18454443
-
In vitro cationic lipid-mediated gene delivery with fluorinated glycerophosphoethanolamine helper lipids.Bioconjug Chem. 2001 Nov-Dec;12(6):949-63. doi: 10.1021/bc010033j. Bioconjug Chem. 2001. PMID: 11716686
-
Lipoplex morphologies and their influences on transfection efficiency in gene delivery.J Control Release. 2007 Nov 20;123(3):184-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.08.022. Epub 2007 Aug 24. J Control Release. 2007. PMID: 17913276 Review.
-
Chemical vectors for gene delivery: a current review on polymers, peptides and lipids containing histidine or imidazole as nucleic acids carriers.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 May;157(2):166-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00288.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19459843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipoplexes' Structure, Preparation, and Role in Managing Different Diseases.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Jun 7;25(5):131. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02850-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38849687 Review.
-
Enhancing natural killer cells proliferation and cytotoxicity using imidazole-based lipid nanoparticles encapsulating interleukin-2 mRNA.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jun 26;35(3):102263. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102263. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39104868 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Lipid Composition of Cationic Liposomes 2X3-DOPE on mRNA Delivery into Eukaryotic Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 20;15(1):8. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010008. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678637 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

