Overcoming Multidrug Resistance of Antibiotics via Nanodelivery Systems
- PMID: 35335962
- PMCID: PMC8950514
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030586
Overcoming Multidrug Resistance of Antibiotics via Nanodelivery Systems
Abstract
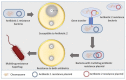
Antibiotic resistance has become a threat to microbial therapies nowadays. The conventional approaches possess several limitations to combat microbial infections. Therefore, to overcome such complications, novel drug delivery systems have gained pharmaceutical scientists' interest. Significant findings have validated the effectiveness of novel drug delivery systems such as polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, metallic nanoparticles, dendrimers, and lipid-based nanoparticles against severe microbial infections and combating antimicrobial resistance. This review article comprises the specific mechanism of antibiotic resistance development in bacteria. In addition, the manuscript incorporated the advanced nanotechnological approaches with their mechanisms, including interaction with the bacterial cell wall, inhibition of biofilm formations, activation of innate and adaptive host immune response, generation of reactive oxygen species, and induction of intracellular effect to fight against antibiotic resistance. A section of this article demonstrated the findings related to the development of delivery systems. Lastly, the role of microfluidics in fighting antimicrobial resistance has been discussed. Overall, this review article is an amalgamation of various strategies to study the role of novel approaches and their mechanism to fight against the resistance developed to the antimicrobial therapies.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; drug delivery; lipid-based nanocarriers; microfluidics; nanoparticles; resistance mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

