Advanced Impedance Spectroscopy for QCM Sensor in Liquid Medium
- PMID: 35336507
- PMCID: PMC8949602
- DOI: 10.3390/s22062337
Advanced Impedance Spectroscopy for QCM Sensor in Liquid Medium
Abstract
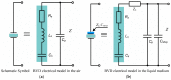
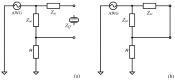
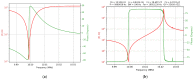
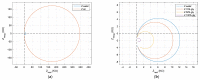
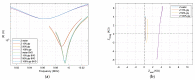
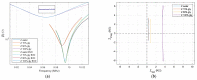
Technological evolution has allowed impedance analysis to become a versatile and efficient method for the precise measurement of the equivalent electrical parameters of the quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). By measuring the dissipation factor, or another equivalent electrical parameter, the QCM sensor provides access to the sample mass per unit area and its physical parameters, thus ensuring a detailed analysis. This paper aims to demonstrate the benefits of advanced impedance spectroscopy concerning the Butterworth-van Dyke (BVD) model for QCM sensors immersed with an electrode in a liquid medium. The support instrument in this study is a fast and accurate software-defined virtual impedance analyzer (VIA) with real-time computing capabilities of the QCM sensor's electric model. Advanced software methods of self-calibration, real-time compensation, innovative post-compensation, and simultaneous calculation by several methods are the experimental resources of the results presented in this paper. The experimental results validate the theoretical concepts and demonstrate both the capabilities of VIA as an instrument and the significant improvements brought by the advanced software methods of impedance spectroscopy analysis related to the BVD model.
Keywords: QCM sensors; impedance analysis; in-liquid measurements; piezoelectric materials; virtual instrumentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kanazawa K.K., Gordon J.G., II The oscillation frequency of a quartz resonator in contact with a liquid. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1985;175:99–105. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)82721-X. - DOI
-
- Reed C.E., Kanazawa K.K., Kaufman J.H. Physical description of a viscoelastically loaded AT-cut quartz resonator. J. Appl. Phys. 1990;68:1993–2001. doi: 10.1063/1.346548. - DOI
-
- Lee C.F., Yan T.R., Wang T.H. Long-term monitoring of Caco-2 cell growth process using a QCM-cell system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012;166:165–171. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2012.02.027. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

