Viral Infection and Respiratory Exacerbation in Children: Results from a Local German Pediatric Exacerbation Cohort
- PMID: 35336898
- PMCID: PMC8955305
- DOI: 10.3390/v14030491
Viral Infection and Respiratory Exacerbation in Children: Results from a Local German Pediatric Exacerbation Cohort
Abstract
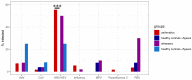
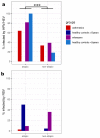
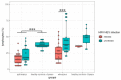
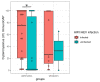
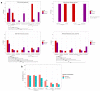
Respiratory viruses play an important role in asthma exacerbation, and early exposure can be involved in recurrent bronchitis and the development of asthma. The exact mechanism is not fully clarified, and pathogen-to-host interaction studies are warranted to identify biomarkers of exacerbation in the early phase. Only a limited number of international exacerbation cohorts were studied. Here, we have established a local pediatric exacerbation study in Germany consisting of children with asthma or chronic, recurrent bronchitis and analyzed the viriome within the nasopharyngeal swab specimens derived from the entire cohort (n = 141). Interestingly, 41% of exacerbated children had a positive test result for human rhinovirus (HRV)/human enterovirus (HEV), and 14% were positive for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). HRV was particularly prevalent in asthmatics (56%), wheezers (50%), and atopic (66%) patients. Lymphocytes were decreased in asthmatics and in HRV-infected subjects, and patients allergic to house dust mites were more susceptible to HRV infection. Our study thus confirms HRV infection as a strong 'biomarker' of exacerbated asthma. Further longitudinal studies will show the clinical progress of those children with a history of an RSV or HRV infection. Vaccination strategies and novel treatment guidelines against HRV are urgently needed to protect those high-risk children from a serious course of disease.
Keywords: asthma; bronchitis; children; exacerbation; human rhinovirus; infection; respiratory syncytial virus; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Vos T., Flaxman A.D., Naghavi M., Lozano R., Michaud C., Ezzati M., Shibuya K., Salomon J.A., Abdalla S., Aboyans V., et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pearce N., Ait-Khaled N., Beasley R., Mallol J., Keil U., Mitchell E., Robertson C., Group I.P.T.S. Worldwide trends in the prevalence of asthma symptoms: Phase III of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Thorax. 2007;62:758–766. doi: 10.1136/thx.2006.070169. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

