Molecular Signaling Mechanisms for the Antidepressant Effects of NLX-101, a Selective Cortical 5-HT1A Receptor Biased Agonist
- PMID: 35337135
- PMCID: PMC8954942
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15030337
Molecular Signaling Mechanisms for the Antidepressant Effects of NLX-101, a Selective Cortical 5-HT1A Receptor Biased Agonist
Abstract
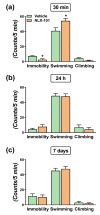
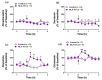
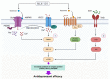
Depression is the most prevalent of the mental illnesses and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) is considered to be the major neurotransmitter involved in its etiology and treatment. In this context, 5-HT1A receptors have attracted interest as targets for therapeutic intervention. Notably the activation of presynaptic 5-HT1A autoreceptors delays antidepressant effects whereas the stimulation of postsynaptic 5-HT1A heteroreceptors is needed for an antidepressant action. NLX-101 (also known as F15599) is a selective biased agonist which exhibits preferred activation of cortical over brain stem 5-HT1A receptors. Here, we used behavioral, neurochemical and molecular methods to examine the antidepressant-like effects in rats of a single dose of NLX-101 (0.16 mg/kg, i.p.). NLX-101 reduced immobility in the forced swim test when measured 30 min but not 24 h after drug administration. NLX-101 increased extracellular concentrations of glutamate and dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex, but no changes were detected in the efflux of noradrenaline or 5-HT. NLX-101 also produced an increase in the activation of pmTOR, pERK1/2 and pAkt, and the expression of PSD95 and GluA1, which may contribute to its rapid antidepressant action.
Keywords: Akt; BDNF; ERK1/2; GluA1; dopamine; glutamate; mTOR; medial prefrontal cortex; p11.
Conflict of interest statement
A.N.-T. is an employee and stockholder of Neurolixis. All other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
NLX-101, a highly selective 5-HT1A receptor biased agonist, mediates antidepressant-like activity in rats via prefrontal cortex 5-HT1A receptors.Behav Brain Res. 2021 Mar 5;401:113082. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.113082. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33358917
-
The 5-HT1A receptor biased agonist, NLX-204, shows rapid-acting antidepressant-like properties and neurochemical changes in two mouse models of depression.Behav Brain Res. 2023 Feb 13;438:114207. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2022.114207. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Behav Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 36368443
-
NLX-112, a highly selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, mediates analgesia and antidepressant-like activity in rats via spinal cord and prefrontal cortex 5-HT1A receptors, respectively.Brain Res. 2018 Jun 1;1688:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29555239
-
Translating biased agonists from molecules to medications: Serotonin 5-HT1A receptor functional selectivity for CNS disorders.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jan;229:107937. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107937. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34174274 Review.
-
Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors as targets for agents to treat psychiatric disorders: rationale and current status of research.CNS Drugs. 2013 Sep;27(9):703-16. doi: 10.1007/s40263-013-0071-0. CNS Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23757185 Review.
Cited by
-
The Serotonin 1A (5-HT1A) Receptor as a Pharmacological Target in Depression.CNS Drugs. 2023 Jul;37(7):571-585. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-01014-7. Epub 2023 Jun 29. CNS Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37386328 Review.
-
Discovery of NLX-266, an Orally Available and Metabolically Stable ERK1/2-Biased 5-HT1AR Agonist with Superior Antidepressant and Antiparkinsonian Activity.J Med Chem. 2025 May 8;68(9):9706-9722. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00484. Epub 2025 Apr 23. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40267318 Free PMC article.
-
[18F]FDG PET metabolic patterns of the rapid-acting antidepressant effects of NLX-101, a 5-HT1A receptor biased agonist.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Sep 1;15(1):336. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03572-4. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40890135 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma-1 Receptors in Depression: Mechanism and Therapeutic Development.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 16;13:925879. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.925879. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rush A.J., Trivedi M.H., Wisniewski S.R., Nierenberg A.A., Stewart J.W., Warden D., Niederehe G., Thase M.E., Lavori P.W., Lebowitz B.D., et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905–1917. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1905. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

