Factors Influencing the Intracellular Concentrations of the Sofosbuvir Metabolite GS-331007 (in PBMCs) at 30 Days of Therapy
- PMID: 35337152
- PMCID: PMC8953593
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15030355
Factors Influencing the Intracellular Concentrations of the Sofosbuvir Metabolite GS-331007 (in PBMCs) at 30 Days of Therapy
Abstract
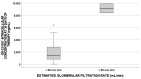
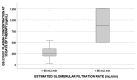
Sofosbuvir (SOF) is an HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor, and GS-331007 is its major metabolite. The aim of this study was to investigate whether clinical and pharmacological factors could influence GS-331007 intracellular (IC) concentrations in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) associated with a sustained virological response in patients treated with SOF and ribavirin (RBV). Drug levels were analyzed using liquid chromatography at different days of therapy, whereas variants in genes encoding transporters and nuclear factors were investigated using real-time PCR. This study enrolled 245 patients treated with SOF; 245 samples were analyzed for pharmacogenetics and 50 were analyzed for IC pharmacokinetics. The GS-331007 IC concentration at 30 days was associated with its plasma concentration determinate at 30, 60 and 90 days of SOF-therapy and with daclatasvir concentrations at 7 days of therapy. No genetic polymorphism affected IC exposure. In linear multivariate analysis, ledipasvir treatment, baseline albumin and estimated glomerular filtration rate were significant predictors of IC exposure. This study presents data on an IC evaluation in a cohort of patients treated with SOF, also considering pharmacogenetics. These results could be useful for regions where SOF-RBV treatment is considered the standard of care; moreover, they could further deepen the knowledge of IC exposure for similar drugs in the future.
Keywords: ABCB1; ABCG2; DAAs; HNF4α; pharmacokinetics; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacogenetics of the anti-HCV drug sofosbuvir: a preliminary study.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018 Jun 1;73(6):1659-1664. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky053. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29509884
-
Efficacy of nucleotide polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir plus the NS5A inhibitor ledipasvir or the NS5B non-nucleoside inhibitor GS-9669 against HCV genotype 1 infection.Gastroenterology. 2014 Mar;146(3):736-743.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.11.007. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24262278 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness, safety and clinical outcomes of direct-acting antiviral therapy in HCV genotype 1 infection: Results from a Spanish real-world cohort.J Hepatol. 2017 Jun;66(6):1138-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28189751
-
A systematic review with meta-analysis: Is ribavirin necessary in sofosbuvir-based direct-acting antiviral therapies for patients with HCV recurrence after liver transplantation?Int J Infect Dis. 2019 Jun;83:56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.03.038. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Int J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30959250
-
Efficacy and safety outcomes of sofosbuvir-based treatment regimens for hepatitis C virus-infected patients with or without cirrhosis from phase III clinical trials.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Apr 12;13:477-497. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S134818. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28442915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hepatitis C (HCV) Agents. [(accessed on 7 February 2022)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548885/

