Metformin Enhances TKI-Afatinib Cytotoxic Effect, Causing Downregulation of Glycolysis, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, and EGFR-Signaling Pathway Activation in Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35337178
- PMCID: PMC8955777
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15030381
Metformin Enhances TKI-Afatinib Cytotoxic Effect, Causing Downregulation of Glycolysis, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, and EGFR-Signaling Pathway Activation in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
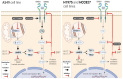
The combination of metformin and TKIs for non-small cell lung cancer has been proposed as a strategy to overcome resistance of neoplastic cells induced by several molecular mechanisms. This study sought to investigate the effects of a second generation TKI afatinib, metformin, or their combination on three adenocarcinoma lung cancer cell lines with different EGFRmutation status. A549, H1975, and HCC827 cell lines were treated with afatinib, metformin, and their combination for 72 h. Afterwards, several parameters were assessed including cytotoxicity, interactions, apoptosis, and EGFR protein levels at the cell membrane and several glycolytic, oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), and EMT expression markers. All cell lines showed additive to synergic interactions for the induction of cytotoxicity caused by the tested combination, as well as an improved pro-apoptotic effect. This effect was accompanied by downregulation of glycolytic, EMT markers, a significant decrease in glucose uptake, extracellular lactate, and a tendency towards increased OXPHOS subunits expression. Interestingly, we observed a better response to the combined therapy in lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1975, which normally have low affinity for TKI treatment. Findings from this study suggest a sensitization to afatinib therapy by metformin in TKI-resistant lung cancer cells, as well as a reduction in cellular glycolytic phenotype.
Keywords: EGFR; afatinib–metformin; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; glycolysis; lung cancer; oxidative phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures







References
-
- Barrón-Barrón F., Guzmán-De Alba E., Alatorre-Alexander J., Aldaco-Sarvider F., Bautista-Aragón Y., Blake-Cerda M., Blanco-Vázquez Y.C., Campos-Gómez S., Corona-Cruz J.F., Iñiguez-García M.A., et al. National Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-small cell lung cancer in early, locally advanced and metastatic stages. Extended version. Salud Publica Mex. 2019;61:359–414. doi: 10.21149/9916. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carrot-Zhang J., Soca-Chafre G., Patterson N., Thorner A.R., Nag A., Watson J., Genovese G., Rodriguez J., Gelbard M.K., Corrales-Rodriguez L., et al. Genetic ancestry contributes to somatic mutations in lung cancers from admixed latin american populations. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:591–598. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arrieta O., Cardona A.F., Martín C., Más-López L., Corrales-Rodríguez L., Bramuglia G., Castillo-Fernandez O., Meyerson M., Amieva-Rivera E., Campos-Parra A.D., et al. Updated frequency of EGFR and KRAS mutations in NonSmall-cell lung cancer in Latin America: The Latin-American consortium for the investigation of lung cancer (CLICaP) J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015;10:838–843. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000481. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

