Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein based on the composite of Cu(OH)2 nanorods arrays as a high-performance surface substrate
- PMID: 35339949
- PMCID: PMC8940256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108106
Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein based on the composite of Cu(OH)2 nanorods arrays as a high-performance surface substrate
Abstract
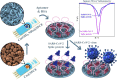
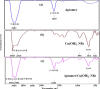
The development of advanced electrode materials and the combination of aptamer with them have improved dramatically the performance of aptasensors. Herein, a new architecture based on copper hydroxide nanorods (Cu(OH)2 NRs) are directly grown on the surface of screen printed carbon electrode (SPCE) using a two-step in situ, very simple and fast strategy and was used as a high-performance substrate for immobilization of aptamer strings, as well as an electrochemical probe to development a label-free electrochemical aptasensor for SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein measurement. The Cu(OH)2 NRs was characterized using X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and electron microscopy (FESEM). In the presence of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, a decrease in Cu(OH)2 NRs-associated peak current was observed that can be owing to the target-aptamer complexes formation and thus blocking the electron transfer of Cu(OH)2 NRs on the surface of electrode. This strategy exhibited wide dynamic range in of 0.1 fg mL-1 to 1.2 µg mL-1 and with a high sensitivity of 1974.43 μA mM-1 cm-2 and low detection limit of 0.03 ± 0.01 fg mL-1 of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein deprived of any cross-reactivity in the presence of possible interference species. In addition, the good reproducibility, repeatability, high stability and excellent feasibility in real samples of saliva and viral transport medium (VTM) were found from the provided aptasensor. Also, the aptasensor efficiency was evaluated by real samples of sick and healthy individuals and compared with the standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method and acceptable results were observed.
Keywords: Aptamer-based sensors; COVID-19; Copper hydroxide nanorods; SARS-CoV-2; Spike glycoprotein.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Manjunatha J.G., Swamy B.E.K., Mamatha G.P., Gilbert O., Shreenivas M.T., Sherigara B.S. Electrocatalytic response of dopamine at mannitol and Triton X-100 modified carbon paste electrode: A cyclic voltammetric study. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009;4:1706–1718.
-
- Jayaprakash G.K., Swamy B.E.K., Rajendrachari S., Sharma S.C., Flores-Moreno R. Dual descriptor analysis of cetylpyridinium modified carbon paste electrodes for ascorbic acid sensing applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2021;334
-
- Manjunathaa J.G., Deraman M., Basri N.H., Talib I.A. Adv. Mater. Res. Trans Tech Publ; 2014. Selective detection of dopamine in the presence of uric acid using polymerized phthalo blue film modified carbon paste electrode; pp. 447–451.
-
- Tigari G., Manjunatha J.G. A surfactant enhanced novel pencil graphite and carbon nanotube composite paste material as an effective electrochemical sensor for determination of riboflavin. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices. 2020;5(1):56–64.
-
- Hareesha N., Manjunatha J.G. Elevated and rapid voltammetric sensing of riboflavin at poly (helianthin dye) blended carbon paste electrode with heterogeneous rate constant elucidation. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020;17(6):1507–1519.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

