Evaluation of Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability, Neurotoxicity, and Potential Cognitive Impairment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa's Virulence Factor Pyocyanin
- PMID: 35340215
- PMCID: PMC8948603
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3060579
Evaluation of Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability, Neurotoxicity, and Potential Cognitive Impairment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa's Virulence Factor Pyocyanin
Abstract
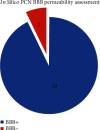
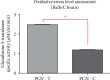
Pyocyanin (PCN) is a redox-active secondary metabolite produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa as its primary virulence factor. Several studies have reported the cytotoxic potential of PCN and its role during infection establishment and progression. Considering its ability to diffuse through biological membranes, it is hypothesized that PCN can gain entry into the brain and induce oxidative stress across the blood-brain barrier (BBB), ultimately contributing towards reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated neurodegeneration. Potential roles of PCN in the central nervous system (CNS) have never been evaluated, hence the study aimed to evaluate PCN's probable penetration into CNS through blood-brain barrier (BBB) using both in silico and in vivo (Balb/c mice) approaches and the impact of ROS generation via commonly used tests: Morris water maze test, novel object recognition, elevated plus maze test, and tail suspension test. Furthermore, evidence for ROS generation in the brain was assessed using glutathione S-transferase assay. PCN demonstrated BBB permeability albeit in minute quantities. A significant hike was observed in ROS generation (P < 0.0001) along with changes in behavior indicating PCN permeability across BBB and potentially affecting cognitive functions. This is the first study exploring the potential role of PCN in influencing the cognitive functions of test animals.
Copyright © 2022 Muhammad Ibrahim Rashid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Pyocyanin induced systemic pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020 May;33(3):915-922. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33191213
-
Cellular Effects of Pyocyanin, a Secreted Virulence Factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Aug 9;8(8):236. doi: 10.3390/toxins8080236. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27517959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.Trends Mol Med. 2004 Dec;10(12):599-606. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.10.002. Trends Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15567330 Review.
-
Inactivation of the potent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin pyocyanin by airway peroxidases and nitrite.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 May 15;302(10):L1044-56. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00172.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22345574
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin activates NRF2-ARE-mediated transcriptional response via the ROS-EGFR-PI3K-AKT/MEK-ERK MAP kinase signaling in pulmonary epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e72528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072528. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24015256 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The two faces of pyocyanin - why and how to steer its production?World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 18;39(4):103. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03548-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36864230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LC-MS/MS determination of pyocyanin-N-acetyl cysteine adduct: application for understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor neutralization.Anal Sci. 2024 May;40(5):891-905. doi: 10.1007/s44211-024-00531-9. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Anal Sci. 2024. PMID: 38472735
-
A biomedical perspective of pyocyanin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: its applications and challenges.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 10;40(3):90. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-03889-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38341389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A purified and lyophilized Pseudomonas aeruginosa derived pyocyanin induces promising apoptotic and necrotic activities against MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Dec 17;21(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01988-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36528623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edelstein M. V., Skleenova E. N., Shevchenko O. V., et al. Spread of extensively resistant VIM-2-positive ST235 Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia: a longitudinal epidemiological and clinical study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases . 2013;13(10):867–876. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70168-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rezzoagli C., Archetti M., Mignot I., Baumgartner M., Kümmerli R. Combining antibiotics with antivirulence compounds can have synergistic effects and reverse selection for antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Biology . 2020;18(8, article e3000805) doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000805. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

