Digital Forensic Investigation of Healthcare Data in Cloud Computing Environment
- PMID: 35340246
- PMCID: PMC8942642
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9709101
Digital Forensic Investigation of Healthcare Data in Cloud Computing Environment
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Digital Forensic Investigation of Healthcare Data in Cloud Computing Environment.J Healthc Eng. 2023 May 24;2023:9782643. doi: 10.1155/2023/9782643. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37266231 Free PMC article.
Abstract
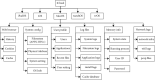
Cloud computing is widely used in various sectors such as finance, health care, and education. Factors such as cost optimization, interoperability, data analysis, and data ownership functionalities are attracting healthcare industry to use cloud services. Security and forensic concerns are associated in cloud environments as sensitive healthcare data can attract the outside attacker and inside malicious events. Storage is the most used service in cloud computing environments. Data stored in iCloud (Apple Inc. Cloud Service Provider) is accessible via a Web browser, cloud client application, or mobile application. Apple Inc. provides iCloud service to synchronize data from MacBook, iPhone, iPad, etc. Core applications such as Mail, Contacts, Calendar, Photos, Notes, Reminders, and Keynote are synced with iCloud. Various operations can be performed on cloud data, including editing, deleting, uploading, and downloading data, as well as synchronizing data between devices. These operations generate log files and directories that are essential from an investigative perspective. This paper presents a taxonomy of iCloud forensic tools that provides a searchable catalog for forensic practitioners to identify the tools that meet their technical requirements. A case study involving healthcare data storage on iCloud service demonstrates that artifacts related to environmental information, browser activities (history, cookies, cache), synchronization activities, log files, directories, data content, and iCloud user activities are stored on a MacBook system. A GUI-based dashboard is developed to support iCloud forensics, specifically the collection of artifacts from a MacBook system.
Copyright © 2022 Anand K. Mishra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Mishra A. K., Pilli E., Govil M. A taxonomy of cloud endpoint forensic tools. Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Digital Forensics; 2018; New Delhi, India. pp. 243–261. - DOI
-
- Mishra A. K., Govil M., Pilli E. A taxonomy of hypervisor forensic tools. Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Digital Forensics; 2020; New Delhi, India. pp. 181–199. - DOI
-
- Lee J., Chung H., Lee C., Lee S. Methodology for digital forensic investigation of iCloud. Information Technology Convergence, Secure and Trust Computing, and Data Management . 2012;180:197–206. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5083-8_25. - DOI
-
- Oestreicher K. A forensically robust method for acquisition of iCloud data. Digital Investigation . 2014;11(Supplement 2):S106–S113. doi: 10.1016/j.diin.2014.05.006. - DOI
-
- Rodriguez-Canseco J., de Fuentes J. M., González-Manzano L., Ribagorda A. MONOCLE- Extensible open-source forensic tool applied to cloud storage cases. Proceedings of the VIII Congreso Iberoamericano de Seguridad Informática Quito; 2015; Ecuador.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources