The Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA) in Diabetes-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 35340338
- PMCID: PMC8943601
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S348055
The Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA) in Diabetes-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
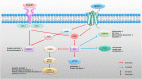
Recent clinical guidelines have emphasized the importance of screening for cognitive impairment in older adults with diabetes, however, there is still a lack of understanding about the drug therapy. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and potential applications may include the treatment of obesity as well as the adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus in combination with insulin. Growing evidence suggests that GLP-1 RA has the potential to treat neurodegenerative diseases, particularly in diabetes-related Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). Here, we review the molecular mechanisms of the neuroprotective effects of GLP-1 RA in diabetes-related degenerative diseases, including AD and PD, and their potential effects.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; cognition; diabetes mellitus; glucagon-like peptide-1.
© 2022 Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

