Restoration of olfactory dysfunctions by nanomaterials and stem cells-based therapies: Current status and future perspectives
- PMID: 35340424
- PMCID: PMC8949739
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314221083414
Restoration of olfactory dysfunctions by nanomaterials and stem cells-based therapies: Current status and future perspectives
Abstract
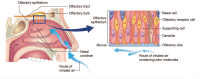
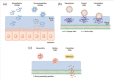
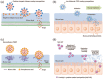
Dysfunction in the olfactory system of a person can have adverse effects on their health and quality of life. It can even increase mortality among individuals. Olfactory dysfunction is related to many factors, including post-viral upper respiratory infection, head trauma, and neurodegenerative disorders. Although some clinical therapies such as steroids and olfactory training are already available, their effectiveness is limited and controversial. Recent research in the field of therapeutic nanoparticles and stem cells has shown the regeneration of dysfunctional olfactory systems. Thus, we are motivated to highlight these regenerative approaches. For this, we first introduce the anatomical characteristics of the olfactory pathway, then detail various pathological factors related to olfactory dysfunctions and current treatments, and then finally discuss the recent regenerative endeavors, with particular focus on nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems and stem cells. This review offers insights into the development of future therapeutic approaches to restore and regenerate dysfunctional olfactory systems.
Keywords: Olfactory dysfunction; nanoparticles; regeneration; stem cells.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factors that modulate olfactory dysfunction.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Jul;13(7):1151-1155. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.235018. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30028314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory Loss and Dysfunction in Ciliopathies: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapies.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(17):3103-3119. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180105102447. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29303074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies towards development of regenerative medicine approaches for olfactory disorders.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Apr 25. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2025-00065. Online ahead of print. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40276849
-
The current possibilities of diagnosing and therapies for olfactory disorders.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024 Jun;25(8):973-983. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2024.2368243. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38935483 Review.
-
Research Progress of Olfactory Nerve Regeneration Mechanism and Olfactory Training.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Mar 5;18:185-195. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S354695. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35281777 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal delivery of macrophage cell membrane cloaked biomimetic drug-nanoparticle system attenuates acute lung injury.J Tissue Eng. 2024 Dec 17;15:20417314241287487. doi: 10.1177/20417314241287487. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2024. PMID: 39698514 Free PMC article.
-
The current status of nanotechnological approaches to therapy and drug delivery in otolaryngology: A contemporary review.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022 Oct 20;7(6):1762-1772. doi: 10.1002/lio2.952. eCollection 2022 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 36544970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Physical and Biological Properties of a Caries-Arresting Liquid Containing Copper Doped Bioglass Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 27;14(6):1137. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061137. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745710 Free PMC article.
-
The role of platelet-rich plasma in biomedicine: A comprehensive overview.iScience. 2025 Jan 3;28(2):111705. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111705. eCollection 2025 Feb 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 39898035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role and Mechanism of Olfactory Stem Cells in the Treatment of Olfactory Disorders.Stem Cells Int. 2025 Apr 24;2025:6631857. doi: 10.1155/sci/6631857. eCollection 2025. Stem Cells Int. 2025. PMID: 40313858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

