Assessing Neonatal Pain with NIPS and COMFORT-B: Evaluation of NICU's Staff Competences
- PMID: 35340544
- PMCID: PMC8942671
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8545372
Assessing Neonatal Pain with NIPS and COMFORT-B: Evaluation of NICU's Staff Competences
Abstract
Background: Pain is considered "the 5th vital sign" that should be regularly assessed in the neonatal intensive care setting. Although over 40 pain assessment tools have been developed for neonates, their implementation in everyday practice is challenging. Epidemiological studies demonstrate that pain is still underassessed and undertreated in European NICUs.
Purpose: To evaluate the interrater and intrarater reliability of the NIPS and COMFORT-B scales among the tertiary NICU's staff members 4 years after their implementation in local pain guidelines with no prior dedicated training.
Methods: Physicians and nurses were invited to evaluate 5 video recordings of infants hospitalized in the intensive care settings, using the NIPS and COMFORT-B scales. The assessment took part twice at a 3-month interval. Interrater reliability was calculated for both scales using Kendall's W coefficient of concordance and Krippendorff's alpha coefficient. Cohen's kappa was used to assess intrarater reliability.
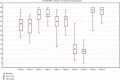
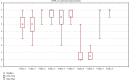
Results: 17 physicians and 19 nurses took part in the study. Interrater agreement for the COMFORT-B scale was above 0.8 for Kendall's W coefficient (p < .01) and above 0.667 for Krippendorff's alpha coefficient. Kendall's W coefficient for the NIPS scores ranged between 0.7 and 0.8 (p < .01). Krippendorff's alpha was above 0.667. Intrarater agreement for both the COMFORT-B and NIPS scales was 0.693 and 0.724, respectively.
Conclusions: Overall, the agreement between our staff members was moderately good for both scales. This is not enough to avoid inadequate pain assessment. More training is needed to improve NICU's staff competences in using pain scales.
Copyright © 2022 Eliza Sarkaria and Dariusz Gruszfeld.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this study.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical