Effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on gingival crevicular fluid levels of Interleukin-35 in patients with periodontitis
- PMID: 35340815
- PMCID: PMC8943404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2022.03.006
Effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on gingival crevicular fluid levels of Interleukin-35 in patients with periodontitis
Abstract
Objective: Interleukin (IL)-35 is a comparatively novel immunosuppressive cytokine produced by T-regulatory cells, the purpose of which in periodontal well being and disease still eludes the researchers. This study intends to measure and compare the levels of IL-35 in gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) taken from periodontitis patients before and at first, second and third week post non-surgical periodontal therapy.
Methodology: ology: Twenty patients having generalized chronic periodontitis (mean age of 36.25 ± 5.12 years) with moderate to severe disease were assessed clinically for the following parameters: plaque index, gingival index, probing pocket depth, and clinical attachment loss. GCF samples were collected from deepest pockets before performing a full mouth non-surgical periodontal therapy. GCF samples were again collected at 1st, 2nd, and 3rd week after non-surgical periodontal therapy and, IL-35 levels in the GCF samples were measured using an ELISA kit.
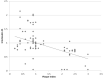
Results: All the clinical parameters improved significantly over time from baseline to 3rd week. The results for plaque index, gingival index, and probing pocket depth were highly significant (p < 0.001) and significant (p < 0.05) for clinical attachment loss. The IL-35 concentration in GCF increased post periodontal therapy from baseline till third week and results were statistically highly significant (p < 0.001). A significant negative correlation (p < 0.001) was found between clinical parameters and IL-35 levels.
Conclusions: With the healing of the previously diseased periodontal tissues, the levels of IL-35 in GCF increases significantly. Therefore, IL-35 can be considered as potential inflammatory marker of periodontal health and disease.
Keywords: Gingival crevicular fluid; Interleukin-35; Non-surgical periodontal therapy; Periodontitis.
© 2022 Craniofacial Research Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adjunctive subantimicrobial dose doxycycline: effect on clinical parameters and gingival crevicular fluid transforming growth factor-beta levels in severe, generalized chronic periodontitis.J Clin Periodontol. 2005 Mar;32(3):244-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00663.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2005. PMID: 15766366 Clinical Trial.
-
Levels of interleukin-1 beta, -8, and -10 and RANTES in gingival crevicular fluid and cell populations in adult periodontitis patients and the effect of periodontal treatment.J Periodontol. 2000 Oct;71(10):1535-45. doi: 10.1902/jop.2000.71.10.1535. J Periodontol. 2000. PMID: 11063385
-
Evaluation of IL-1β, IL-1ra, and IL-10 levels and outcome of periodontal therapy in chronic periodontitis with familial Mediterranean fever.Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Jan;21(1):469-475. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1816-1. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Clin Oral Investig. 2017. PMID: 27068409
-
Soluble Neuropilin-1 in gingival crevicular fluid from periodontitis patients: An exploratory cross-sectional study.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021 Jan-Mar;11(1):84-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2020.11.015. Epub 2020 Nov 27. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021. PMID: 33384917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on the serum and crevicular fluid interleukin-10 levels in chronic periodontitis - A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2021 Nov-Dec;15(6):34-46. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2021. PMID: 34912186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-39 and IL-35 gingival crevicular fluid levels in diabetic patients with generalized periodontitis.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Jan 30;28(2):124. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05484-3. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38286978 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

