C5 ventral ramus block for clavicle surgery: How low concerning the volume can we go?
- PMID: 35340971
- PMCID: PMC8944372
- DOI: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_362_20
C5 ventral ramus block for clavicle surgery: How low concerning the volume can we go?
Abstract
Background and aims: Clinical case reports mention 3-5 ml of local anesthetic (LA) at the cervical root 5 (C5) for surgical anesthesia essential for clavicle surgeries with reasonable success. A volume of 5 ml LA has been shown to cause hemidiaphragmatic paresis.
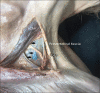
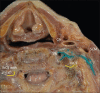
Material and methods: We implement the 3-5 ml LA for awake clavicle surgeries along with a supraclavicular nerve (SCN) block with another 2 ml. To understand the spread of injectate, we conducted anatomic macroscopic dissection on Theil based cadavers. Post ultrasound injection of 3 ml of blue latex in one cadaver and green latex in the other, we dissected one cadaver and the other cadaver underwent a cross-section.
Results: Dissection confirmed a vertical spread of dye more caudad than cephalad. There was no neuraxial spread visualized in the cross-section. The phrenic nerve (PN) was not stained in both cadavers, but a possibility exists depending on its course.
Conclusion: Based on this limited study we recommend a volume of LA of 3 ml at the level of C5 and another 2 ml at the level SCN of LA for clavicle surgeries.
Keywords: Cadaver; cervical root; clavicle; phrenic nerve; regional anesthesia; supraclavicular nerve; ultrasonography.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kline JP. Ultrasound-guided placement of combined superficial cervical plexus and selective C5 nerve root catheters:A novel approach to treating distal clavicle surgical pain. AANA J. 2013;81:19–22. - PubMed
-
- Stundner O, Meissnitzer M, Brummett CM, Moser S, Forstner R, Koköfer A, et al. Comparison of tissue distribution, phrenic nerve involvement, and epidural spread in standard- vs low-volume ultrasound-guided interscalene plexus block using contrast magnetic resonance imaging:A randomized, controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2016;116:405–12. - PubMed
-
- Falyar CR, Abercrombie C, Becker R, Biddle C. Intrathecal spread of injectate following an ultrasound-guided selective C5 nerve root injection in a human cadaver model. AANA J. 2016;84:80–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
