Coronary Artery and Cardiac Disease in Patients With Type 2 Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35341327
- PMCID: PMC9010024
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.058542
Coronary Artery and Cardiac Disease in Patients With Type 2 Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort Study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Coronary Artery and Cardiac Disease in Patients With Type 2 Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort Study.Circulation. 2022 Apr 19;145(16):e841. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001070. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35436138 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Type 2 myocardial infarction is caused by myocardial oxygen supply-demand imbalance, and its diagnosis is increasingly common with the advent of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. Although this diagnosis is associated with poor outcomes, widespread uncertainty and confusion remain among clinicians as to how to investigate and manage this heterogeneous group of patients with type 2 myocardial infarction.
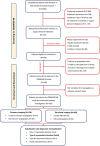
Methods: In a prospective cohort study, 8064 consecutive patients with increased cardiac troponin concentrations were screened to identify patients with type 2 myocardial infarction. We excluded patients with frailty or renal or hepatic failure. All study participants underwent coronary (invasive or computed tomography angiography) and cardiac (magnetic resonance or echocardiography) imaging, and the underlying causes of infarction were independently adjudicated. The primary outcome was the prevalence of coronary artery disease.
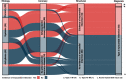
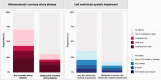
Results: In 100 patients with a provisional diagnosis of type 2 myocardial infarction (median age, 65 years [interquartile range, 55-74 years]; 43% women), coronary and cardiac imaging reclassified the diagnosis in 7 patients: type 1 or 4b myocardial infarction in 5 and acute myocardial injury in 2 patients. In those with type 2 myocardial infarction, median cardiac troponin I concentrations were 195 ng/L (interquartile range, 62-760 ng/L) at presentation and 1165 ng/L (interquartile range, 277-3782 ng/L) on repeat testing. The prevalence of coronary artery disease was 68% (63 of 93), which was obstructive in 30% (28 of 93). Infarct-pattern late gadolinium enhancement or regional wall motion abnormalities were observed in 42% (39 of 93), and left ventricular systolic dysfunction was seen in 34% (32 of 93). Only 10 patients had both normal coronary and normal cardiac imaging. Coronary artery disease and left ventricular systolic dysfunction were previously unrecognized in 60% (38 of 63) and 84% (27 of 32), respectively, with only 33% (21 of 63) and 19% (6 of 32) on evidence-based treatments.
Conclusions: Systematic coronary and cardiac imaging of patients with type 2 myocardial infarction identified coronary artery disease in two-thirds and left ventricular systolic dysfunction in one-third of patients. Unrecognized and untreated coronary or cardiac disease is seen in most patients with type 2 myocardial infarction, presenting opportunities for initiation of evidence-based treatments with major potential to improve clinical outcomes.
Registration: URL: https://www.
Clinicaltrials: gov; Unique identifier: NCT03338504.
Keywords: cardiac imaging techniques; echocardiography; magnetic resonance imaging; myocardial infarction.
Figures

Comment in
-
Zooming in on the Enigmas of Type 2 Myocardial Infarction.Circulation. 2022 Apr 19;145(16):1201-1204. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059454. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35436133 No abstract available.
-
Response by Bularga et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Coronary Artery and Cardiac Disease in Patients With Type 2 Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort Study".Circulation. 2022 Nov 8;146(19):e258-e259. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.061692. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 36343102 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Agirbasli and Aksoy Regarding Article, "Coronary Artery and Cardiac Disease in Patients With Type 2 Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort Study".Circulation. 2022 Nov 8;146(19):e257. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060625. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 36343105 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, Jaffe AS, Apple FS, Galvani M, Katus HA, Newby LK, Ravkilde J, Chaitman B, et al. ; Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Redefinition of Myocardial Infarction. Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2007;116:2634–2653. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187397 - PubMed
-
- Clopidogrel in Unstable Angina to Prevent Recurrent Events (CURE) Trial Investigators. Effects of clopidogrel in addition to aspirin in patients with acute coronary syndromes without ST-segment elevation. N Engl J Med. 2011;345:494–502. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa010746 - PubMed
-
- Roe MT, Messenger JC, Weintraub WS, Cannon CP, Fonarow GC, Dai D, Chen AY, Klein LW, Masoudi FA, McKay C, et al. Treatments, trends, and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction and percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:254–263. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.008 - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, White HD; ESC Scientific Document Group. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Eur Heart J. 2019;40:237–269. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehy462 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- FS/14/78/31020/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/16/14/32023/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CH/11/2/28733/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CH/F/21/90010/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/V007254/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/20/10/34966/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/CRTF/21/24273/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RE/18/5/34216/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/16/10/32375/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- WT103782AIA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/V007017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS/RTF/21/30028/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/19/46/34445/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/16/75/32533/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/ICRF/20/26002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CH/09/002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

