Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome
- PMID: 35341691
- PMCID: PMC8942460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2022.103433
Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome
Abstract
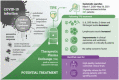
The risk of mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is largely related to an excessive immune response, resulting in a hyperinflammatory and hypercoagulable condition collectively referred to as cytokine storm syndrome (CSS). Management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 has included attempts to abate this process, prevent disease progression, and reduce mortality. In this context, therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) offers an approach to eliminate inflammatory factors and cytokines, offset the pathologic coagulopathy, and reduce the CSS effects. The aim of this review is to analyze available data on the use of TPE for the treatment of CSS in patients with COVID-19. Systematic searches of PubMed, Scopus and COVID-19 Research were conducted to identify articles published between March 1, 2020 and May 26, 2021 reporting the use of TPE for the treatment of COVID-19-induced CSS. A total of 34 peer-reviewed articles (1 randomized controlled trial, 4 matched case-control series, 15 single-group case series, and 14 case reports), including 267 patients, were selected. Despite the low evidence level of the available data, TPE appeared to be a safe intervention for critically ill patients with COVID-19-induced CSS. Although inconsistencies exist between studies, they showed a general trend for decreased interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, ferritin, D-dimer, and fibrinogen levels and increased lymphocyte counts following TPE, supporting the immunomodulatory effect of this treatment. Moreover, TPE was associated with improvements in clinical outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19. While TPE may offer a valuable option to treat patients with COVID-19-induced CSS, high-quality randomized controlled clinical trials are needed to confirm its potential clinical benefits, feasibility, and safety. Moreover, clear criteria should be established to identify patients with CSS who might benefit from TPE.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine storm syndrome; Efficacy; Penn grading; SARS-CoV-2; Safety; Therapeutic plasma exchange.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest M. Beraud and A. Bah are employees of Terumo Blood and Cell Technologies Europe N.V. (Belgium). M. Lozano on behalf of his institution, Clinic Research Foundation, has received research support from Terumo Blood and Cell Technologies and Sanofi-Genzyme, and speaker honoraria from Grífols. S. Al Hashami and Philip Keith have nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of COVID-19 induced cytokine storm: the first Moroccan experience.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 25;23(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08816-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 38007416 Free PMC article.
-
The association between therapeutic plasma exchange and the risk of mortality among patients critically ill with COVID-19: a meta-analysis.F1000Res. 2021 Dec 14;10:1280. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.74972.1. eCollection 2021. F1000Res. 2021. PMID: 35083038 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot study of therapeutic plasma exchange for serious SARS CoV-2 disease (COVID-19): A structured summary of a randomized controlled trial study protocol.Trials. 2020 Jun 8;21(1):506. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04454-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32513290 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of penn class 3 and 4 cytokine release syndrome complicating COVID-19.Respir Med. 2020 Dec;175:106188. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106188. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33190086 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Inflammatory Markers and Acute Phase Reactants in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 29;59(5):867. doi: 10.3390/medicina59050867. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37241099 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of COVID-19 induced cytokine storm: the first Moroccan experience.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 25;23(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08816-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 38007416 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking the role of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in the critically ill.Transfus Apher Sci. 2023 Feb;62(1):103521. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2022.103521. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Transfus Apher Sci. 2023. PMID: 35941021 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Benefits of plasma exchange on mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2022 Sep;122:332-336. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.014. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Int J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35709964 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Adsorption with the MTx.100 Column in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Study and Propensity Score Analysis.J Intensive Care Med. 2025 Mar;40(3):314-319. doi: 10.1177/08850666241280031. Epub 2024 Sep 12. J Intensive Care Med. 2025. PMID: 39267408 Free PMC article.
-
The application of therapeutic plasma exchange in sepsis and septic shock: A narrative review.Sci Prog. 2025 Jul-Sep;108(3):368504251352747. doi: 10.1177/00368504251352747. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40696820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update. Available at: 〈https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situati... [Accessed on March 23, 2021].
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous