Blockade of corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptors in the infralimbic cortex prevents stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking in male Wistar rats: Evidence of interaction between CRF1 and orexin receptor signaling
- PMID: 35341789
- PMCID: PMC9176217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109046
Blockade of corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptors in the infralimbic cortex prevents stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking in male Wistar rats: Evidence of interaction between CRF1 and orexin receptor signaling
Abstract
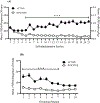
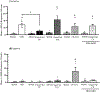
Alcohol use dysregulates responsivity to stress, which is mediated by corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF). With repeated cycles of alcohol use, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis becomes hyporesponsive, rendering individuals vulnerable to the reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior during stressful episodes. Orexin (Orx; also called hypocretin) plays a well-established role in regulating diverse physiological processes, including stress, and interacts with CRF. The infralimbic cortex (IL) is a CRF-rich region. Anatomical evidence suggests that CRF and Orx interact in this area. To test the behavioral implication of CRF and Orx transmission in the IL during the stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior, male Wistar rats were trained to self-administer 10% alcohol for 3 weeks. The rats then underwent two weeks of extinction training (identical to the alcohol self-administration sessions, but alcohol was withheld). The day after the last extinction session, the rats received a bilateral intra-IL injection of the CRF1 receptor antagonist CP154,526 (0.6 μg/0.5 μl/side), the dual Orx receptor antagonist TCS1102 (15 μg/0.5 μl/side), or their combination and then were tested for the footshock stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior. CP154,526 significantly prevented reinstatement, but TCS1102 did not produce such an effect. Interestingly, the co-administration of TCS1102 and CP154,526 reversed the effect of CP154,526 alone, and footshock stress induced a significant increase in Crhr1 and Hcrtr2 mRNA expression in the IL. These results demonstrate a functional interaction between Orx receptor and CRF1 receptor signaling and suggest that CRF1 receptor antagonism may ameliorate stress-induced alcohol-seeking behavior.
Keywords: Alcohol; CP154,526; Corticotropin-releasing factor; Orexin; TCS1102.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blockade of orexin receptors in the infralimbic cortex prevents stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behaviour in alcohol-dependent rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;180(11):1500-1515. doi: 10.1111/bph.16015. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36537731 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis and corticotropin-releasing factor stress system on cue-induced relapse to alcohol seeking.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 5;788:84-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.06.020. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27316790 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretins regulate the anxiogenic-like effects of nicotine and induce reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 10;30(6):2300-10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5724-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20147556 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Role of CRF-Hcrt Interaction in the Infralimbic Cortex in the Emergence and Maintenance of Compulsive Alcohol-Seeking Behavior.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Feb;44(2):354-367. doi: 10.1111/acer.14264. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 31840823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress and arousal: the corticotrophin-releasing factor/hypocretin circuitry.Mol Neurobiol. 2005 Dec;32(3):285-94. doi: 10.1385/MN:32:3:285. Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16385142 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for independent actions of the CRF and ghrelin systems in binge-like alcohol drinking in mice.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 2;138:111341. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2025.111341. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40139339
-
Withdrawal from chronic alcohol impairs the serotonin-mediated modulation of GABAergic transmission in the infralimbic cortex in male rats.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Sep;199:106590. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106590. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38996987 Free PMC article.
-
LY2444296, a κ-opioid receptor antagonist, selectively reduces alcohol drinking in male and female Wistar rats with a history of alcohol dependence.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 9;14(1):5804. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56500-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38461355 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin releasing factor and drug seeking in substance use disorders: Preclinical evidence and translational limitations.Addict Neurosci. 2022 Dec;4:100038. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100038. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Addict Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36531188 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Alcohol Drinking Drives Sex-Specific Differences in Affective Behavior and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Activity in CRF1:Cre:tdTomato Transgenic Rats.eNeuro. 2023 Jul 13;10(7):ENEURO.0055-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0055-23.2023. Print 2023 Jul. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37414553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker HC (2012). Effects of alcohol dependence and withdrawal on stress responsiveness and alcohol consumption. Alcohol Res, 34(4), 448–458. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23584111 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

