Accuracy of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) to diagnose COVID-19, a meta-analysis
- PMID: 35341958
- PMCID: PMC8949659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105498
Accuracy of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) to diagnose COVID-19, a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the accuracy of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) in determining coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19).
Methods: As of January 31, 2022, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Science Direct, Wiley and Springer Link were searched. Sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratio (LR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and area under the summary receiver-operating characteristic (AUC) curve were used to assess the accuracy of CRISPR.
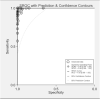
Results: According to the inclusion criteria, 5857 patients from 54 studies were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity, specificity and AUC were 0.98, 1.00 and 1.00, respectively. For CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins-12, the sensitivity, specificity was 0.96, 1.00, respectively. For Cas-13, the sensitivity and specificity were 0.99 and 0.99.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed that the diagnostic performance of CRISPR is close to the gold standard, and it is expected to meet the Point of care requirements in resource poor areas.
Keywords: COVID-19; CRISPR; Meta analysis; SARS-Cov-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic efficiency of RPA/RAA integrated CRISPR-Cas technique for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 26;17(10):e0276728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276728. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36288366 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of CRISPR-Based Assays for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Yonsei Med J. 2022 May;63(5):480-489. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.5.480. Yonsei Med J. 2022. PMID: 35512751 Free PMC article.
-
Label-free Colorimetric Detection of Viral RNA Based on Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats and Gold Nanoparticles with a Portable Device.Langmuir. 2024 Jun 4;40(22):11534-11540. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c00657. Epub 2024 May 17. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 38758706
-
[Recent advances in clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-based detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2].Se Pu. 2022 Sep;40(9):773-781. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.08001. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 36156623 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
CRISPR-Based COVID-19 Testing: Toward Next-Generation Point-of-Care Diagnostics.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Apr 30;11:663949. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.663949. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33996635 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic efficiency of RPA/RAA integrated CRISPR-Cas technique for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 26;17(10):e0276728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276728. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36288366 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Technology in Detection of COVID-19.Cureus. 2022 Sep 13;14(9):e29138. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29138. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36259008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR Assays for Disease Diagnosis: Progress to and Barriers Remaining for Clinical Applications.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jul;10(20):e2301697. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301697. Epub 2023 May 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37162202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Detection Using CRISPR Technology: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Mol Diagn Ther. 2024 Nov;28(6):777-790. doi: 10.1007/s40291-024-00741-x. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Mol Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 39212838
References
-
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus(2019-nCoV) Situation Report-10. Data as reported by 30 January 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Repor-51. Data as reported by national authorities by 10 AM CET 11 March 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 - 4 May 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous