The impact of radiomics in diagnosis and staging of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 35342883
- PMCID: PMC8943316
- DOI: 10.1177/26317745221081596
The impact of radiomics in diagnosis and staging of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most aggressive tumours, and better risk stratification among patients is required to provide tailored treatment. The meaning of radiomics and texture analysis as predictive techniques are not already systematically assessed. The aim of this study is to assess the role of radiomics in PC.
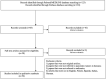
Methods: A PubMed/MEDLINE and Embase systematic review was conducted to assess the role of radiomics in PC. The search strategy was 'radiomics [All Fields] AND ("pancreas" [MeSH Terms] OR "pancreas" [All Fields] OR "pancreatic" [All Fields])' and only original articles referred to PC in humans in the English language were considered.
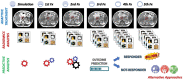
Results: A total of 123 studies and 183 studies were obtained using the mentioned search strategy on PubMed and Embase, respectively. After the complete selection process, a total of 56 papers were considered eligible for the analysis of the results. Radiomics methods were applied in PC for assessment technical feasibility and reproducibility aspects analysis, risk stratification, biologic or genomic status prediction and treatment response prediction.
Discussion: Radiomics seems to be a promising approach to evaluate PC from diagnosis to treatment response prediction. Further and larger studies are required to confirm the role and allowed to include radiomics parameter in a comprehensive decision support system.
Keywords: decision supporting system; pancreatic cancer; radiomics.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur J Cancer 2018; 103: 356–387. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020; 70: 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Pancreatic Cancer: Cancer Stat facts, https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed 3 April 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

