Cytotoxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles: From Mechanisms and Methods of Evaluation to Pathological Manifestations
- PMID: 35343105
- PMCID: PMC9165481
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202106049
Cytotoxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles: From Mechanisms and Methods of Evaluation to Pathological Manifestations
Abstract
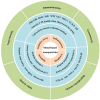
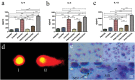
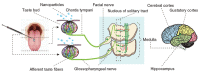
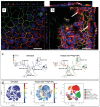
Metal-based nanoparticles (NPs) are particularly important tools in tissue engineering-, drug carrier-, interventional therapy-, and biobased technologies. However, their complex and varied migration and transformation pathways, as well as their continuous accumulation in closed biological systems, cause various unpredictable toxic effects that threaten human and ecosystem health. Considerable experimental and theoretical efforts have been made toward understanding these cytotoxic effects, though more research on metal-based NPs integrated with clinical medicine is required. This review summarizes the mechanisms and evaluation methods of cytotoxicity and provides an in-depth analysis of the typical effects generated in the nervous, immune, reproductive, and genetic systems. In addition, the challenges and opportunities are discussed to enhance future investigations on safer metal-based NPs for practical commercial adoption.
Keywords: cytotoxic effect; cytotoxicity; evaluation method; metal-based nanoparticle; toxic mechanism.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
