Clinical efficacy and safety of interleukin-6 receptor antagonists (tocilizumab and sarilumab) in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35343397
- PMCID: PMC9037226
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2059405
Clinical efficacy and safety of interleukin-6 receptor antagonists (tocilizumab and sarilumab) in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
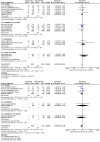
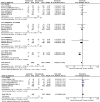
This study investigated the efficacy and safety of interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonists with standard care treatment in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The randomized controlled trials were identified through systematic searches of electronic databases through February 10, 2022. In total, 17 trials comprising 8,614 patients were included. Compared with exclusive standard care or placebo, IL-6 receptor antagonists with standard of care treatment were associated with a significantly reduced all-cause mortality at 28 days (pooled risk ratios [RR], 0.88; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.82-0.95; 17 studies) and progression to invasive mechanical ventilation (RR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.71-0.88; nine studies). Particularly, the subgroup of patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 showed a significant mortality benefit (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.81-0.96; four studies) and a reduced risk for mechanical ventilation (RR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.70-0.91; three studies) with tocilizumab treatment. The frequency of serious adverse events was lower in the tocilizumab treatment group than in the standard of care treatment group (RR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.71-0.97; 11 studies), with no significant difference in the sarilumab treatment group (RR, 1.12; 95% CI, 0.89-1.40; four studies). Our meta-analysis demonstrated that tocilizumab treatment showed promising results in reducing 28-day mortality and progression to mechanical ventilation in patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19, without the burden of serious adverse events.Trial registration: Clinical Trials Registry India identifier: CTRI/2020/05/025369.The proper registration is PROSPERO: registration number CRD42021294120.
Keywords: COVID-19; meta-analysis; sarilumab; systematic review; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
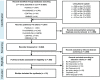

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
