Trends and hot topics in radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging from 2011-2021: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers
- PMID: 35344133
- PMCID: PMC8958482
- DOI: 10.1007/s11604-022-01268-z
Trends and hot topics in radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging from 2011-2021: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers
Abstract
Purpose: To spotlight the trends and hot topics looming from the highly cited papers in the subject category of Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging with bibliometric analysis.
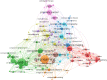
Materials and methods: Based on the Essential Science Indicators, this study employed a bibliometric method to examine the highly cited papers in the subject category of Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging in Web of Science (WoS) Categories, both quantitatively and qualitatively. In total, 1325 highly cited papers were retrieved and assessed spanning from the years of 2011 to 2021. In particular, the bibliometric information of the highly cited papers based on WoS database such as the main publication venues, the most productive countries, and the top cited publications was presented. An Abstract corpus was built to help identify the most frequently explored topics. VoSviewer was used to visualize the co-occurrence networks of author keywords.
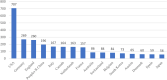
Results: The top three active journals are Neuroimage, Radiology and IEEE T Med Imaging. The United States, Germany and England have the most influential publications. The top cited publications unrelated to COVID-19 can be grouped in three categories: recommendations or guidelines, processing software, and analysis methods. The top cited publications on COVID-19 are dominantly in China. The most frequently explored topics based on the Abstract corpus and the author keywords with the great link strengths overlap to a great extent. Specifically, phrases such as magnetic resonance imaging, deep learning, prostate cancer, chest CT, computed tomography, CT images, coronavirus disease, convolutional neural network(s) are among the most frequently mentioned.
Conclusion: The bibliometric analysis of the highly cited papers provided the most updated trends and hot topics which may provide insights and research directions for medical researchers and healthcare practitioners in the future.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; Highly cited papers; Medical imaging; Nuclear medicine; Radiology.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Japan Radiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global vaccine research and application hotspots and trends: a systematic bibliometric analysis based on SCIE highly cited papers.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 22;15(1):e094935. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094935. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39843371 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of core competencies associated nursing management publications.J Nurs Manag. 2022 Oct;30(7):2869-2880. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13795. Epub 2022 Sep 20. J Nurs Manag. 2022. PMID: 36076321 Review.
-
Radiology During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mapping Radiology Literature in 2020.Curr Med Imaging. 2023;19(2):175-181. doi: 10.2174/1573405618666211230105631. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 34967299
-
Trends and hot topics in linguistics studies from 2011 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 11;13:1052586. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1052586. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36710766 Free PMC article.
-
Top 100 most frequently cited papers in liver cancer: a bibliometric analysis.ANZ J Surg. 2020 Jan;90(1-2):21-26. doi: 10.1111/ans.15414. Epub 2019 Sep 3. ANZ J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31480098 Review.
Cited by
-
Bibliometric and scientometric analysis of PSMA-targeted radiotheranostics: knowledge mapping and global standing.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 1;14:1397790. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1397790. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39011478 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of the current status and trends on medical hyperspectral imaging.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 19;10:1235955. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1235955. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37795419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research landscape on artificial intelligence in echocardiography from 1997 to 2024: Bibliometric analysis.Digit Health. 2025 Jun 30;11:20552076251351201. doi: 10.1177/20552076251351201. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40605994 Free PMC article.
-
Race analysis in swimming: understanding the evolution of publications, citations and networks through a bibliometric review.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Jun 13;6:1413182. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1413182. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 38939752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating brain tumor classification using MRI: a scientometric analysis of selected articles from 2015 to 2024.Neuroradiology. 2025 Jul 18. doi: 10.1007/s00234-025-03685-z. Online ahead of print. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 40679613 Review.
References
-
- Aksnes DW, Sivertsen G. The effect of highly cited papers on national citation indicators. Scientometrics. 2004;59:213–224. doi: 10.1023/B:SCIE.0000018529.58334.eb. - DOI
-
- Danell R. Can the quality of scientific work be predicted using information on the author's track record? J Am Soc Inf Sci Tec. 2011;62:50–60. doi: 10.1002/asi.21454. - DOI
-
- Csajbók E, Berhidi A, Vasas L, Schubert A. Hirsch-index for countries based on Essential Science Indicators data. Scientometrics. 2007;73:91–117. doi: 10.1007/s11192-007-1859-9. - DOI
-
- Fu H, Chuang K, Wang M, Ho Y. Characteristics of research in China assessed with Essential Science Indicators. Scientometrics. 2011;88:841–862. doi: 10.1007/s11192-011-0416-8. - DOI
-
- Ma R, Ni C, Qiu J. Scientific research competitiveness of world universities in computer science. Scientometrics. 2008;76:245–260. doi: 10.1007/s11192-007-1913-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical