Synthesis and Characterization of Size- and Charge-Tunable Silver Nanoparticles for Selective Anticancer and Antibacterial Treatment
- PMID: 35344328
- PMCID: PMC8990520
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c01100
Synthesis and Characterization of Size- and Charge-Tunable Silver Nanoparticles for Selective Anticancer and Antibacterial Treatment
Abstract
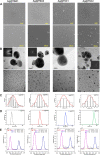
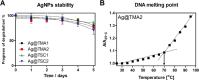
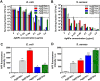
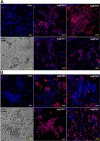
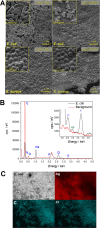
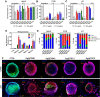
Advances in the research of nanoparticles (NPs) with controlled charge and size are driven by their potential application in the development of novel technologies and innovative therapeutics. This work reports the synthesis, characterization, and comprehensive biological evaluation of AgNPs functionalized by N,N,N-trimethyl-(11-mercaptoundecyl) ammonium chloride (TMA) and trisodium citrate (TSC). The prepared AgNPs were well characterized in terms of their morphological, spectroscopic and functional properties and biological activities. The implementation of several complementary techniques allowed not only the estimation of the average particle size (from 3 to 40 nm depending on the synthesis procedure used) but also the confirmation of the crystalline nature of the NPs and their round shape. To prove the usefulness of these materials in biological systems, cellular uptake and cytotoxicity in microbial and mammalian cells were determined. Positively charged 10 nm Ag@TMA2 revealed antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 0.17 μg/mL and complete eradication of Escherichia coli (7 logs) for Ag@TMA2 at a concentration of 0.50 μg/mL, whereas negatively charged 10 nm Ag@TSC1 was effective against Gram-positive bacteria (MIC = 0.05 μg/mL), leading to inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus at relatively low concentrations. In addition, the largest 40 nm Ag@TSC2 was shown to exhibit pronounced anticancer activity against murine colon carcinoma (CT26) and murine mammary gland carcinoma (4T1) cells cultured as 2D and 3D tumor models and reduced toxicity against human HaCaT keratinocytes. Among the possible mechanisms of AgNPs are their ability to generate reactive oxygen species, which was further evaluated in vitro and correlates well with cellular accumulation and overall activity of AgNPs. Furthermore, we confirmed the anticancer efficacy of the most potent Ag@TSC2 in hiPSC-derived colonic organoids and demonstrated that the NPs are biocompatible and applicable in vivo. A pilot study in BALB/c mice evidenced that the treatment with Ag@TSC2 resulted in temporary (>60 days) remission of CT26 tumors.
Keywords: advanced cellular models; antibacterial activity; anticancer activity; organoids; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mycosynthesis, characterization, anticancer and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles from endophytic fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 May 9;14:3427-3438. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S200817. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31190801 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria of biomimetically coated silver nanoparticles.Langmuir. 2011 Aug 2;27(15):9165-73. doi: 10.1021/la201200r. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Langmuir. 2011. PMID: 21736306
-
Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extract and its biomedical applications.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;46(6):1163-1170. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1362417. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28784039
-
A Comprehensive Review of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles as Effective Antibacterial Agents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 29;17(9):1134. doi: 10.3390/ph17091134. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) as a Double-Edged Sword: Synthesis, Factors Affecting, Mechanisms of Toxicity and Anticancer Potentials-An Updated Review till March 2025.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04688-w. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40512370 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Plant Species on the Synthesis and Characterization of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: A Comparative Study of Brassica oleracea, Corylus avellana, and Camellia sinensis.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Dec 5;14(23):1954. doi: 10.3390/nano14231954. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39683344 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Application of Silver Nanoparticles for Enhancing Phototherapy Outcomes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;18(7):970. doi: 10.3390/ph18070970. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Desmochloris edaphica Strain CCAP 6006/5 for the Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Insights into the Anticancer and Antibacterial Efficacy.Molecules. 2024 Aug 7;29(16):3750. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163750. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202829 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles in Therapeutics and Beyond: A Review of Mechanism Insights and Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;14(20):1618. doi: 10.3390/nano14201618. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in antibacterial applications of nanozymes.Front Chem. 2024 Sep 23;12:1478273. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1478273. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39376729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Regiel-Futyra A.; Dąbrowski J. M.; Mazuryk O.; Śpiewak K.; Kyzioł A.; Pucelik B.; Brindell M.; Stochel G. Bioinorganic antimicrobial strategies in the resistance era. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 351, 76–117. 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.05.005. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

