HIPK2 directs cell type-specific regulation of STAT3 transcriptional activity in Th17 cell differentiation
- PMID: 35344430
- PMCID: PMC9168845
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2117112119
HIPK2 directs cell type-specific regulation of STAT3 transcriptional activity in Th17 cell differentiation
Abstract
SignificanceSTAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) is a master transcription factor that organizes cellular responses to cytokines and growth factors and is implicated in inflammatory disorders. STAT3 is a well-recognized therapeutic target for human cancer and inflammatory disorders, but how its function is regulated in a cell type-specific manner has been a major outstanding question. We discovered that Stat3 imposes self-directed regulation through controlling transcription of its own regulator homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (Hipk2) in a T helper 17 (Th17) cell-specific manner. Our validation of the functional importance of the Stat3-Hipk2 axis in Th17 cell development in the pathogenesis of T cell-induced colitis in mice suggests an approach to therapeutically treat inflammatory bowel diseases that currently lack a safe and effective therapy.
Keywords: STAT3; Th17 cell differentiation; chromatin biology; gene transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
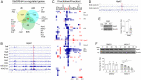
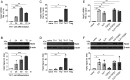

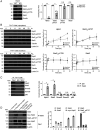
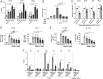
References
-
- Yang J., Sundrud M. S., Skepner J., Yamagata T., Targeting Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 35, 493–500 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Ishigame H., et al. , Differential roles of interleukin-17A and -17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity 30, 108–119 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Ivanov I. I., et al. , The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 126, 1121–1133 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

