Epidemiological characteristic of rubella by age group during 12 years after the national introduction of rubella vaccine in Hangzhou, China
- PMID: 35344684
- PMCID: PMC9225618
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2054208
Epidemiological characteristic of rubella by age group during 12 years after the national introduction of rubella vaccine in Hangzhou, China
Abstract
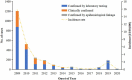
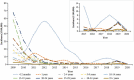
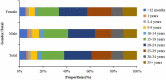
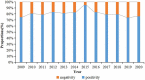
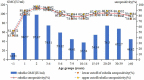
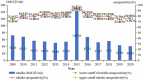
This study aimed to evaluate the implementation and impact of rubella-containing vaccine (RCV) by describing the rubella epidemiology and seroepidemiology in Hangzhou. We collected rubella cases of Hangzhou in the Information System for Disease Control and Prevention in China between 2009 and 2020, and performed a descriptive analysis. We applied a multi-stage stratified random sampling method to recruit participants for serological tests of rubella. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) was used to detect Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against rubella in serum samples. Univariate and multivariate analyses are used to detect the association between the level of rubella IgG and related factors. The incidence of rubella cases per million population decreased from 15.8 in 2009 to .1 in 2020. The proportion of rubella cases in women of childbearing age was higher than in men. A total of 4,362 subjects were tested serologically for rubella. The percentage of people whose rubella IgG antibody titers were above the minimum protective level (20 IU/ml) was 80.60% (95% CI: 79.4%-81.8%) and the geometric mean concentration (GMC) for rubella IgG was 58.34 IU/ml. The data indicated that Hangzhou had made good progress toward the elimination of rubella, whereas women of childbearing age still had a higher proportion of rubella cases, which might lead to increased risk of subsequent CRS. The positive rate and GMC of rubella IgG were significantly influenced by age and immunization history of RCV. Therefore, we should stress the importance of pushing forward the campaign for supplementary vaccination of rubella in adults.
Keywords: China; Rubella; Rubella vaccine; epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Do adolescents need a rubella vaccination campaign? Rubella serosurvey among healthy children in Hangzhou, China.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug;19(2):2254536. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2254536. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37750387 Free PMC article.
-
Seroepidemiology of tetanus in Hangzhou from 2009 to 2018.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Nov 1;16(11):2670-2676. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1738170. Epub 2020 May 27. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32460603 Free PMC article.
-
Seroepidemiology of varicella in Hangzhou, China in the vaccine era.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018;14(10):2464-2471. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1477909. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018. PMID: 30019992 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological profile and progress toward rubella elimination in China. 10 years after nationwide introduction of rubella vaccine.Vaccine. 2018 Apr 12;36(16):2079-2085. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29550193
-
Targeting rubella for elimination.Indian J Public Health. 2012 Oct-Dec;56(4):269-72. doi: 10.4103/0019-557X.106413. Indian J Public Health. 2012. PMID: 23354136 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology of Rubella Virus in a Fragile and Conflict-affected Setting - A Retrospective Analysis of 11 Years Case-based Data in South Sudan.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 9;12(5):ofaf221. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf221. eCollection 2025 May. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40406370 Free PMC article.
-
Rubella antibody levels in the healthy Chinese population: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 12;15:1472189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1472189. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39600703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA , et al. Vaccines. 7th ed. Holland: Elsevier; 2017. p. 970–8. ISBN: 9780323357616.
-
- World Health Organization . Measles and rubella strategic framework 2021–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020. https://measlesrubellainitiative.org/measles-rubella-strategic-framework....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
