Broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by an inhalable bispecific single-domain antibody
- PMID: 35344711
- PMCID: PMC8907017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.009
Broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by an inhalable bispecific single-domain antibody
Abstract
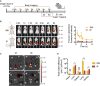
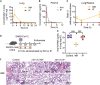
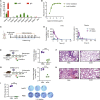
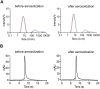
The effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and therapeutic antibodies have been limited by the continuous emergence of viral variants and by the restricted diffusion of antibodies from circulation into the sites of respiratory virus infection. Here, we report the identification of two highly conserved regions on the Omicron variant receptor-binding domain recognized by broadly neutralizing antibodies. Furthermore, we generated a bispecific single-domain antibody that was able to simultaneously and synergistically bind these two regions on a single Omicron variant receptor-binding domain as revealed by cryo-EM structures. We demonstrated that this bispecific antibody can be effectively delivered to lung via inhalation administration and exhibits exquisite neutralization breadth and therapeutic efficacy in mouse models of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Importantly, this study also deciphered an uncommon and highly conserved cryptic epitope within the spike trimeric interface that may have implications for the design of broadly protective SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and therapeutics.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; bispecific antibody; broad neutralization; inhalation; single-domain antibody.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.L., Y.W., and T.Y. are listed as inventors on two patent applications related to this work.
Figures
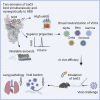


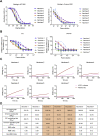
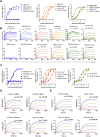
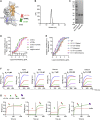
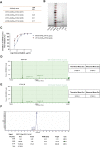

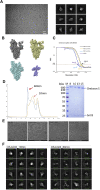
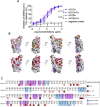
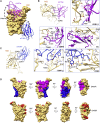
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

